Page 52 - 南京医科大学学报自然科学版
P. 52
第42卷第2期
·198 · 南 京 医 科 大 学 学 报 2022年2月
100 循环闭塞的老年患者的临床基线数据,对后循环取
栓预后,以及其他未纳入的潜在因素并未有效论
80
证。因此,需要更大规模研究来阐明机械取栓对
( % ) 60 AIS合并AF的老年患者的治疗效果。
老年 AF 患者前循环急性缺血性脑卒中时,如
灵敏度 40 合并基线 NIHSS 评分高和/或非阵发性 AF 时,选择
取栓治疗要更慎重。此外,需进一步提高老年 AF
20
患者的抗凝率预防脑卒中。
AUC=0.92,95% CI:0.84~1.00,P<0.001
0 [参考文献]
0 20 40 60 80 100
1-特异度(%) [1] 陶秋成,王远成,秦 智,等. CT 成像下左心耳形态和
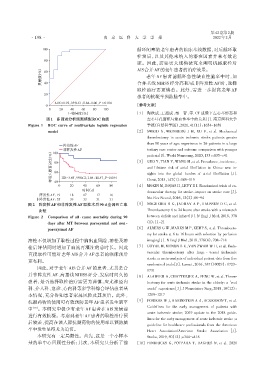
图1 多因素分析预测模型ROC曲线 左心耳孔面积与缺血性卒中的关系[J]. 南京医科大学
Figure 1 ROC curve of multivariate logistic regression 学报(自然科学版),2021,41(11):1654-1658
model [2] SWEID A,WEINBERG J H,XU V,et al. Mechanical
thrombectomy in acute ischemic stroke patients greater
than 90 years of age:experience in 26 patients in a large
阵发性AF
非阵发性AF tertiary care center and outcome comparison with younger
( % ) 100 [3] GUO Y,TIAN Y,WANG H,et al. Prevalence,incidence,
patients[J]. World Neurosurg,2020,133:e835-e41
存活人数百分比 60 HR=3.45,95%CI:1.04~11.47,P=0.034 and lifetime risk of atrial fibrillation in China:new in⁃
80
sights into the global burden of atrial fibrillation[J].
Chest,2015,147(1):109-119
40
10 20 40 60 80 [4] MOKIN M,ROJAS H,LEVY E I. Randomized trials of en⁃
时间(d)
dovascular therapy for stroke ⁃ impact on stroke care[J].
阵发性AF:19 18 17 17 16
Nat Rev Neurol,2016,12(2):86-94
非阵发性AF:55 39 33 31 31
图 2 阵发性 AF 和非阵发性 AF 取栓术后 90 d 全因死亡率 [5] NOGUEIRA R G,JADHAV A P,HAUSSEN D C,et al.
比较 Thrombectomy 6 to 24 hours after stroke with a mismatch
Figure 2 Comparison of all ⁃ cause mortality during 90 between deficit and infarct[J]. N Engl J Med,2018,378
days after MT between paroxysmal and non ⁃ (1):11-21
paroxysmal AF [6] ALBERS G W,MARKS M P,KEMP S,et al. Thrombecto⁃
my for stroke at 6 to 16 hours with selection by perfusion
溶栓不仅增加了取栓过程中脑出血风险,溶栓及溶 imaging[J]. N Engl J Med,2018,378(8):708-718
栓后评估同时增加了血流再灌注的总时长。因此 [7] GOYAL M,MENON B K,VAN ZWAM W H,et al. Endo⁃
直接取栓可能对老年 AIS 合并 AF 患者的临床预后 vascular thrombectomy after large ⁃ vessel ischaemic
stroke:a meta⁃analysis of individual patient data from five
更有利。
randomised trials[J]. Lancet,2016,387(10029):1723-
因此,对于老年 AIS 合并 AF 的患者,尤其是合
1731
并非阵发性 AF、高基线 NIHSS 评分、发病时间久的 [8] ALAWIEH A,CHATTERJEE A,FENG W,et al. Throm⁃
患者,是否选择取栓治疗需更为谨慎,应尤神经内 bectomy for acute ischemic stroke in the elderly:a‘real
科、介入科、急诊、心内科等多学科综合评估患者基 world’experience[J]. J Neurointerv Surg,2018,10(12):
本情况,充分告知患者家属风险及其预后。此外, 1209-1217
抗凝药物的使用可有效预防老年AF 患者发生脑卒 [9] POWERS W J,RABINSTEIN A A,ACKERSON T,et al.
Guidelines for the early management of patients with
中 [10] 。本研究中极少有老年 AF 患者在 AIS 发病前
acute ischemic stroke:2019 update to the 2018 guide⁃
进行有效抗凝。考虑到老年AF 患者的取栓治疗预
lines for the early management of acute ischemic stroke:a
后较差,提高在该人群抗凝药物的使用率以预防脑
guideline for healthcare professionals from the American
卒中发生显得尤为迫切。
Heart Association/American Stroke Association [J].
本研究有一定局限性。首先,这是一个小样本 Stroke,2019,50(12):e344-e418
量的单中心回顾性分析;其次,本研究只分析了前 [10] HINDRICKS G,POTPARA T,DAGRES N,et al. 2020