Page 68 - 南京医科大学学报自然科学版
P. 68
第44卷第1期
· 62 · 南 京 医 科 大 学 学 报 2024年1月
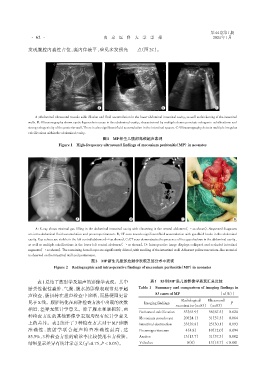
发现腹腔内囊性占位,囊内伴液平,壁见多发强光 点(图2C)。
A B C
A:Abdominal ultrasound reveals wide dilation and fluid accumulation in the lower abdominal intestinal cavity,as well as thickening of the intestinal
walls. B:Ultrasonography shows cystic hypoechoic areas in the abdominal cavity,characterized by multiple dense punctate echogenic calcifications and
strong echogenicity of the posterior wall. There is also significant fluid accumulation in the intestinal spaces. C:Ultrasonography detects multiple irregular
calcifications within the abdominal cavity.
图1 MP新生儿腹部高频超声表现
Figure 1 High⁃frequency ultrasound findings of meconium peritonitis(MP)in neonates
A B C D
A:X⁃ray shows minimal gas filling in the abdominal intestinal cavity with clustering in the central abdomen(→ as shown). Suspected diagnoses
are intra⁃abdominal fluid accumulation and pneumoperitoneum. B:CT scan reveals significant fluid accumulation with gas⁃fluid levels in the abdominal
cavity. Gas echoes are visible in the left central abdomen(→ as shown). C:CT scan demonstrates the presence of free gas shadows in the abdominal cavity,
as well as multiple calcifications in the lower left central abdomen(→ as shown). D:Intraoperative image displays collapsed and occluded intestinal
segments(→ as shown). The remaining bowel loops are significantly dilated,with swelling of the intestinal wall. Adherent yellow meconium⁃like material
is observed on the intestinal wall and peritoneum.
图2 MP新生儿腹部放射学表现及部分术中表现
Figure 2 Radiographic and intraoperative findings of meconium peritonitis(MP)in neonates
表1总结了放射学及超声的影像学表现。其中 表1 83例MP患儿的影像学表现汇总比较
胎粪性假性囊肿、气腹、腹水的影像表现常见于超 Table 1 Summary and comparison of imaging findings in
83 cases of MP [n(%)]
声检查,肠扭转在超声检查中诊断,而肠梗阻更常
见于X线。腹腔钙化在两种检查方法中出现的次数 Imaging findings Radiological Ultrasound P
examination(n=83) (n=83)
相近,差异无统计学意义。除了腹水和肠扭转,两
Peritoneal calcification 53(63.9) 56(67.5) 0.624
种检查方法的其他影像学表现均没有统计学意义
Meconium pseudocyst 20(24.1) 31(37.3) 0.064
上的差异。表 2 统计了 3 种检查方式对于 MP 诊断 Intestinal obstruction 33(39.8) 25(30.1) 0.193
准 确 性 ,放 射 学 联 合 超 声 检 查 准 确 性 最 高 ,达 Pneumoperitoneum 4(4.8) 10(12.0) 0.094
85.5%,3 种检查方法的确诊率比较使用卡方检验, Ascites 13(15.7) 31(37.3) 0.002
结果显示差异有统计学意义(χ =8.75,P < 0.05)。 Volvulus 0(0) 13(15.7) < 0.001
2