Page 127 - 南京医科大学自然版
P. 127
第44卷第11期 黄嘉燕,梅钰婷,胡春梅. 间充质干细胞来源外泌体在骨组织修复中的应用[J].
2024年11月 南京医科大学学报(自然科学版),2024,44(11):1590-1598 ·1593 ·
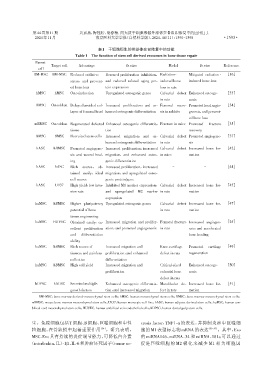
表1 干细胞衍生的外泌体在骨修复中的功能
Table 1 The function of stem cell derived exosomes in bone tissue repair
Parent
Target cell Advantage In vitro Model In vivo Reference
cell
BM⁃MSC BM⁃MSC Reduced oxidative Rescued proliferation inhibition, Radiation⁃ Mitigated radiation ⁃ [16]
stress,and prevent⁃ and reduced related aging pro⁃ induced bone induced bone loss
ed bone loss tein expression loss in rats
hMSC hMSC Osteoinduction Upregulated osteogenic genes Calvarial defect Enhanced osteoge⁃ [33]
in rats nesis
BMSC Osteoblast Delayed/avoided col⁃ Increased proliferation,and en⁃ Femoral necro⁃ Promotedlocalangio⁃ [34]
lapse of femoral head hanced osteogenic differentiation sis in rabbits genesis,and prevent⁃
ed bone loss
mBMSC Osteoblast Regenerated defected Enhanced osteogenic differentia⁃ Fracture in mice Promoted fracture [35]
tissue tion recovery
BMSC BMSC Recruited stem cells Increased migration, and en⁃ Calvarial defect Promoted angiogene⁃ [37]
hanced osteogenic differentiation in rats sis
hASC hBMSC Promoted angiogene⁃ Increased proliferation,increased Calvarial defect Increased bone for⁃ [42]
sis and wound heal⁃ migration,and enhanced osteo⁃ in mice mation
ing genic differentiation
hASC hASC Rich source, ob⁃ Increased proliferation,increased - - [44]
tained easily,ideal migration,and upregulated osteo⁃
cell source genic protein/gene
hASC U937 High yield,low inva⁃ Inhibited M1 marker expression,Calvarial defect Increased bone for⁃ [45]
sion rate and upregulated M2 marker in rats mation
expression
huMSC hBMSC Higher pluripotency Upregulated osteogenic genes Calvarial defect Increased bone for⁃ [47]
potential of bone in rats mation
tissue engineering
huMSC HUVEC Obtained easily,ex⁃ Increased migration and prolifer⁃ Femoral fracture Increased angiogen⁃ [25]
cellent proliferation ation,and promoted angiogenesis in rats esis,and accelerated
and differentiation bone healing
ability
huMSC hBMSC Rich source of Increased migration and Knee cartilage Promoted cartilage [49]
tissues,and painless proliferation,and enhanced defect in rats regeneration
collection differentiation
huMSC hBMSC High cell yield Increased migration and Critical⁃sized Enhanced osteoge⁃ [50]
proliferation calvarial bone nesis
defect in rats
hDPSC hADSC Secreted multiple Enhanced osteogenic differentia⁃ Mandibular de⁃ Increased bone for⁃ [51]
growth factors tion,and increased migration fect in rats mation
BM⁃MSC:bone marrow derived⁃mesenchymal stem cells;hMSC:human mesenchymal stem cells;BMSC:bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells;
mBMSC:mouse bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells;U937:human monocyte cell line;hASC:human adipose derived stem cells;huMSC:human um⁃
bilical cord mesenchymal stem cells;HUVEC:human umbilical vein endothelial cells;hDPSC:human dental pulp stem cells.
生。免疫细胞包括T细胞、B细胞、巨噬细胞和中性 crosis factor,TNF)⁃α的表达,并抑制炎症中巨噬细
粒细胞,在骨缺损中起着重要作用 [54] 。研究表明, 胞的 M1 表型标志物 mRNA 的表达 [55-57] 。其中,Exo
MSC⁃Exo 具有持续的炎症调节能力,可降低白介素 的 miRNA146、miRNA⁃34 和 miRNA⁃181a 可以通过
(interleukin,IL)⁃1β、IL⁃6和肿瘤坏死因子(tumor ne⁃ 促进巨噬细胞的 M2 极化来减少 M1 相关细胞因