Page 66 - 南京医科大学学报自然科学版
P. 66
第44卷第3期
·356 · 南 京 医 科 大 学 学 报 2024年3月
表3 PD患者伴发抑郁的多因素Logistic回归分析
Table 3 Multivariate logistic regression analysis of PD patients with depression
Variables Regression coefficient Standard error z Wald χ 2 P Odds Ratio 95% CI
PNI -0.177 0.052 -3.405 11.597 0.001 0.838 0.756-0.928
NLR -0.301 0.140 -2.147 04.608 0.032 1.351 1.026-1.777
LED -0.001 0.001 -2.007 04.027 0.045 1.001 1.000-1.003
UPDRS⁃Ⅲ -0.043 0.013 -3.291 10.828 0.001 1.044 1.018-1.071
0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
Points
PNI
62 60 58 56 54 52 50 48 46 44 42 40 38 36
NLR
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
LED
0 200 600 1 000 1 400 1 800
UPDRS⁃Ⅲ
5 15 25 35 45 55 65 75
Total points
0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 180 200 220 240
Risk scores
0.1 0.20.3 0.5 0.7 0.8 0.9
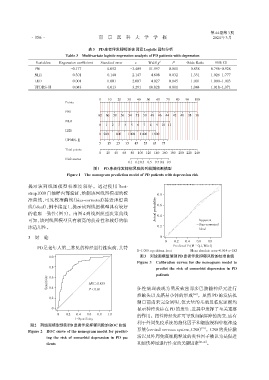
图1 PD患者伴发抑郁风险的列线图预测模型
Figure 1 The nomogram prediction model of PD patients with depression risk
提示该列线图模型校准度较好。通过使用 Boot⁃
strap1000自抽样内部验证,绘制该列线图模型的校 0.8
准曲线,可见校准曲线(bias⁃corrected)接近理想曲
线(ideal),斜率接近1,提示该列线图模型具有较好 Actual probability 0.6
的临床一致性(图 3)。由图 4 列线图模型决策曲线 0.4
可知,该列线图模型具有较高的获益性和较好的临 Apparent
Bias⁃corrected
床适用性。 0.2
Ideal
3 讨 论 0
00 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8
PD是老年人第二常见的神经退行性疾病,其特 Predicted Pr{M^0jJ,Wi=1}
B=1 000 repetitions,boot Mean absolute error=0.014 n=182
图3 列线图模型预测PD患者伴发抑郁风险的校准曲线
1.0
Figure 3 Calibration curves for the nomogram model to
predict the risk of comorbid depression in PD
0.8
patients
Sensitivity 0.4 AUC:0.835 征性病理表现为黑质致密部多巴胺能神经元进行
0.6
P < 0.01
性缺失以及路易小体的形成 [22] 。虽然PD 的发病机
0.2
制目前尚未完全阐明,但大量的基础及临床证据均
0 显示神经炎症在PD的发生、进展中发挥了至关重要
00 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 的作用。慢性神经炎症可导致血脑屏障的改变,这有
1-Specificity
利于外周免疫系统的趋化因子和细胞浸润中枢神经
图2 列线图模型预测PD患者伴发抑郁风险的ROC曲线
[23]
Figure 2 ROC curve of the nomogram model for predict⁃ 系统(central nervous system,CNS) 。CNS的炎症激
ing the risk of comorbid depression in PD pa⁃ 活以及外周免疫细胞释放的炎性因子被认为是促进
tients 和加快神经退行性变的关键因素 [24-26] 。