Page 114 - 南京医科大学自然版
P. 114
第44卷第6期
·850 · 南 京 医 科 大 学 学 报 2024年6月
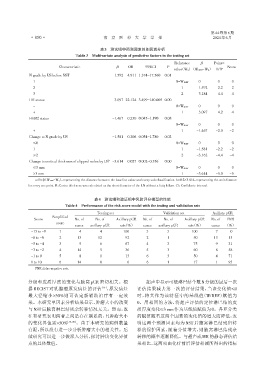
表3 测试组中预测因素的多因素分析
Table 3 Multivariate analysis of predictive factors in the testing set
Reference β Point=
Characteristic β OR 95%CI P Score
value(Wij) (WiREF-Wij) D/B a
N grade by US before NST 1.592 4.911 1.374-17.560 0.01 -
1 0=W1REF 0.00 0. -0
2 1 -1.592 -2.2 -2
3 2 -3.184 -4.4 -4
HR status 3.097 22.124 3.499-140.005 0.00
- 0=W2REF 0.00 0. -0
+ 1 -3.097 -4.2 -4
HER2 status -1.467 0.230 0.045-1.190 0.08
- 0=W3REF 0.00 0. -0
+ 1 -1.467 -2.0 -2
Change to N grade by US -1.581 0.206 0.054-1.780 0.02
≤0 0=W4REF 0.00 0. -0
1 1 -1.581 -2.2 -2
≥2 2 -3.162 -4.4 -4
b
Change to cortical thickness of clipped nodes by US -3.614 0.027 0.002-0.356 0.00
≤3 mm 0=W5REF 0.00 0. -0
>3 mm 1 -3.614 -5.0 -5
a:D=β(WiREF-Wij),representing the distance between the baseline value and every sub classification. b=0.2×3.614,representing the unit distance
for every one point. B:Cortex thickness was calculated as the short diameter of the LN without a fatty hilum. CI:Confidente interval.
表4 测试组和验证组中风险评分模型的性能
Table 4 Performance of the risk score model with the testing and validation sets
Testing set Validation set Axillary pCR
Simplified
Score No. of No. of Axillary pCR No. of No. of Axillary pCR No. of FNR
score
cases axillary pCR rate(%) cases axillary pCR rate(%) cases (%)
-13 to -9 1 04 04 100 3 3 100 07 00
-8 to -6 2 13 12 092 2 1 050 13 13
-5 to -4 3 09 06 067 4 3 075 09 31
-3 to -2 4 14 05 036 5 3 060 08 58
-1 to 0 5 08 01 013 6 3 050 04 71
1 to 10 6 14 00 000 6 1 017 01 95
FNR:false⁃negative rate.
分级和皮质厚度的变化与腋窝 pCR 密切相关。根 超声中显示可疑淋巴结个数N分级的最后一次
据 RECIST 对乳腺癌原发病灶的评估 [19] ,原发病灶 评估结果减去第一次的评估结果,当该变化值≤0
最大径缩小>30%则可认定新辅助治疗有一定效 时,将其作为该特征中的基线值(WiREF)赋值为
果。本研究单因素分析结果显示,肿瘤大小的改变 0。用相同的方法,将超声评估的定位淋巴结的皮
与NST 后腋窝淋巴结残余转移情况无关。然而,既 质厚度变化≤3 mm作为基线值赋值为0。各亚分类
往有研究表明两者之间是存在联系的,且肿瘤大小 的赋值随着这两个因素的变化值的增大而降低,表
[18,20]
的变化界值需>50% 。由于本研究的病例数量 明这两个预测因素均为 NST 后腋窝淋巴结残留转
有限,所以没有进一步分析肿瘤大小的相关性。后 移的保护因素,随着分值增大,则腋窝淋巴结残余
续研究可以进一步做深入分析,探讨肿块变化界值 转移的概率逐渐降低。与超声或MR的静态评估结
点的具体数值。 果相比,这两项由化疗前后评估相减所得出的指标