Page 70 - 南京医科大学自然版
P. 70
第44卷第6期
·806 · 南 京 医 科 大 学 学 报 2024年6月
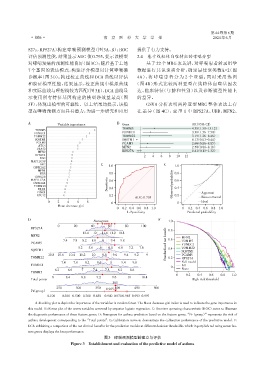
S27a,RPS27A)构建哮喘预测模型(图 3A、B);ROC 提供了有力支持。
评估预测性能,结果显示AUC 值0.795,提示该模型 2.4 基于线粒体自噬特征的哮喘分型
对哮喘发病的预测性能良好(图3C);随后基于上述 基于 22 个 MRG 表达谱,对哮喘患者转录组学
7 个基因的表达模式,构建评分模型以计算哮喘确 数据进行共识聚类分析,确定最佳聚类数 k=2(图
诊概率(图 3D);构建校正曲线和 DCA 曲线以评估 4A),将哮喘患者分为 2 个亚型;同时采用热图
和验证模型性能,结果显示,校正曲线中模拟曲线 (图 4B)形式比较两种亚型在线粒体自噬基因表
和实际曲线与理想线较为匹配(图3E),DCA曲线显 达、临床特征(年龄和性别)以及诊断模型性能上
示使用所有特征基因构建的模型净效益最高(图 的差异。
3F),体现出模型的可靠性。以上结果均提示,该模 GSVA 分析表明两种亚型 MRG 整体表达上存
型在哮喘预测方面具有潜力,为进一步研究和应用 在 差 异(图 4C),亚 型 1 中 RPS27A、UBB、MFN2、
A Variable importance B Gene OR(95% CI)
TOMM5 4.38(1.50-13.12)
TOMM5
FUNDC1 FUNDC1 3.36(1.56-7.50)
TOMM22 TOMM22 3.19(1.26-8.46)
SQSTM1 SQSTM1 0.13(0.03-0.44)
PGAM5 PGAM5 2.66(0.86-8.85)
ATG5 MFN2 2.50(0.80-8.18)
UBA52
MFN2 RPS27A 0.41(0.13-1.32)
RPS27A 2 4 6 8 10 12
UBC
MAP1LC3B
SRC C 1.0 E 1.0
CSNK2A2
MFN1
UBB 0.8 0.8
CSNK2B
MAP1LC3A 0.6 0.6
CSNK2A1 Sensitivity Observed probability
TOMM20
ULK1 0.4 0.4
PINK1 Apparent
ATG12 0.2 0.2
AUC:0.795 Bias⁃corrected
0 2 4 6 8 ldeal
0 0
Mean decrease gini
0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0
1-Specificity Predicted probability
D Nomogram F 1.0
0 20 40 60 80 100
RPS27A 0.8
12.4 12 11.6 11.2 10.8
MFN2 MFN2
7.4 7.8 8.2 8.6 9 9.4 9.8 0.6 TOMM5
PGAM5 Standardized net benefit FUNDC1
5.2 5.6 6 6.4 6.8 7.2 7.6 0.4 TOMM22
SQSTM1 SQSTM1
10.8 10.6 10.4 10.2 10 9.8 9.6 9.4 9.2 9 PGAM5
TOMM22 0.2 RPS27A
7.4 7.8 8.2 8.6 9 9.4 9.8 Full model
FUNDC1 All
0
6.2 6.6 7 7.4 7.8 8.2 8.6 None
TOMM5
00 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0
8 8.4 8.8 9.2 9.6 10 10.4
Total points High risk threshold
395
250 300 350 0.965 400 450 500
Pr(group)
0.100 0.300 0.500 0.700 0.850 0.940 0.970 0.985 0.993 0.997
A:Ranking plot to depict the importance of the variables in random forest. The Mean decrease gini index is used to indicate the gene importance in
this model. B:Forest plot of the seven variables screened by stepwise logistic regression. C: Receiver operating characteristic(ROC)curve to illustrate
the diagnostic performance of these feature genes. D:Nomogram for asthma prediction based on the feature genes.“Pr(group)”represents the risk of
asthma development corresponding to the“Total points”. E:Calibration curve to demonstrate the calibration performance of the predictive model. F:
DCA exhibiting a comparison of the net clinical benefits for the prediction models at different decision thresholds,which in purplish red using seven fea⁃
ture genes displays the best performance.
图3 哮喘预测模型的建立与评估
Figure 3 Establishment and evaluation of the predictive model of asthma