Page 12 - 南京医科大学学报自然科学版
P. 12
第41卷第6期
·790 · 南 京 医 科 大 学 学 报 2021年6月
A B
Pathways in cancer 5 275
Neuroactive ligand⁃receptor interaction 4 220
Nicotine addiction
HTLV⁃I infection Num of Genes 3 165
Morphine addiction 2 110
Tuberculosis GeneNumber
50
Chemical carcinogenesis 1 055
100
Epstein⁃Barr virus infection 150
Taste transduction 200 0 biological adhesion biological phase biological regulation cell aggregation cell killing cellular process developmental process growth localization metabolic process reproduction reproductive process response to stimulus rhythmic process signaling cell cell junction cell part extracellular matrix extracellular region membrane membrane part nucleoid organelle organelle part other organism other organism part supram
structural moecule activity
molecular transducer activity
transcription factor activity, protein binding
nucleic acid binding transcnption factor activity
detoxification
behavior
multiceilular organismal process
locomotion
multi⁃organism process
molecular function regulator
binding
macromolecular complex
Pathway Chagas disease(American trypanosomiasis) QValue cellular component organization of biogenesis immune system process presynaptic process invoived in synaptic transmission single⁃organism process extracellular matrix component extracellular region part membrane⁃enclosed lumen chemoattractant activity chemorepellent activity electron carrier activity molecular transducer egulater signal transducer activity translation regulator activity
250
Influenza A
Amphetamine addiction 0.006
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy(HCM) 0.004
Toxoplasmosis
0.002 Biological Process Cellular Component Molecular Function
Dopaminergic synapse
Central carbon metabolism in cancer
Dilated cardiomyopathy(DCM)
Hepatitis B
Retrograde endocannabinoid signaling
Choline metabolism in cancer
0.175 0.200 0.225 0.250 0.275
Rich Factor
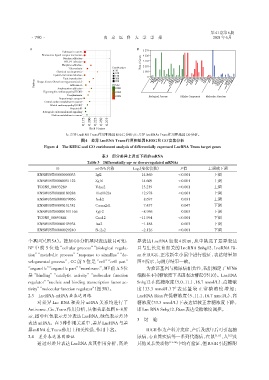
A:差异LncRNA Trans作用靶基因KEEG 分析;B:差异LncRNAs Trans作用靶基因GO分析。
图4 差异LncRNA Trans作用靶基因KEEG和GO富集分析
Figure 4 The KEEG and GO enrichment analysis of differentially expressed LncRNA Trans target genes
表3 部分差异上调或下调的mRNA
Table 3 Differentially up⁃ or down⁃regulated mRNAs
ID mRNA名称 Log2 (变化倍数) P值 上调或下调
ENSMUST00000000033 Igf2 014.860 <0.001 上调
ENSMUST00000051122 Zg16 014.609 <0.001 上调
TCONS_00033289 Vdac2 013.239 <0.001 上调
ENSMUST00000180288 Hist1h2br 0-12.9780 <0.001 上调
ENSMUST00000079056 Anb2 0-8.697 0.031 上调
ENSMUST00000101581 Cacna2d1 0-7.437 0.047 下调
ENSMUST000001531166 Fgfr2 0-8.966 0.003 下调
TCONS_00093844 Gna12 -11.994 <0.001 下调
ENSMUST00000105934 Ins2 0-1.188 0.003 下调
ENSMUST00000029240 Slc2a2 0-2.126 <0.001 下调
个基因)(图5A)。按照GO分析基因表达数目可知: 异表达 LncRNA 如表 4 所示,从中挑选了差异表达
BP 中 前 5 位 是“cellular process”“biological regula⁃ 且与生长发育相关的 LncRNA Snhg12、LncRNA Ri⁃
tion”“metabolic process”“response to simullus”“de⁃ an在IUGR、正常新生小鼠中进行验证,表达结果如
velopmental process”,CC 前 5 位是“cell”“cell part” 图9所示,与测序结果一致。
“organelle”“organelle part”“membrane”,MF前五5位 为验证基因与糖尿病相关性,我们测定了MIN6
是“binding”“catalytic activity”“molecular function 细胞在不同糖浓度下基因表达情况(图10)。LncRNA
regulator”“nucleic and binding transcription factor ac⁃ Snhg12 在低糖浓度(5.0、11.1、16.7 mmol/L)、高糖浓
tivity”“molecular function regulator”(图5B)。 度(33.3 mmol/L)下表达量较正常糖浓度增加;
2.3 LncRNA⁃mRNA共表达网络 LncRNA Rian 在低糖浓度(5、11.1、16.7 mmol/L)、高
对差异 Lnc RNA 和差异 mRNA 关系均进行了 糖浓度(33.3 mmol/L)下表达量较正常糖浓度下降,
Antisense、Cis、Trans作用分析,具体关系如图6~8所 即Lnc RNA Snhg12、Rian表达受糖浓度调控。
示,图中红色表示差异表达LncRNA,绿色表示差异
3 讨 论
表达mRNA。在3种作用关系中,差异LncRNA与差
异mRNA在Trans作用上相关性强,作用丰富。 IUGR作为产科并发症,产后及成年后可引起糖
[12]
2.4 差异表达基因验证 尿病、心血管疾病等一系列代谢病,在鼠 [5,11] 、人 及
通过对差异表达 LncRNA 及其作用分析,高差 其他灵长类动物 [13-14] 中均有验证,但IUGR引起糖耐