Page 42 - 南京医科大学学报自然科学版
P. 42
第41卷第9期
·1308 · 南 京 医 科 大 学 学 报 2021年9月
A B
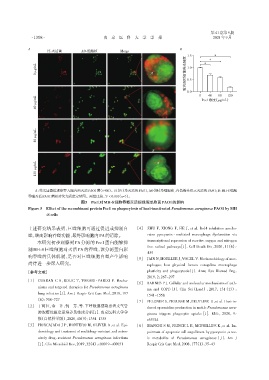
PI⁃灭活菌 AO⁃细胞核 Merge *
胞内相对细菌荧光强度 1.5
μg/mL 1.0 * *
0 0.5
0.0 0 40 80 120
40 μg/mL Pec1浓度(μg/mL)
80 μg/mL
μg/mL
120
A:荧光显微镜观察吞入胞内的灭活PAO1菌(×400)。PI(红)染灭活的PAO1,AO(绿)染细胞核,白色箭头指示灭活的PAO1;B:MH⁃S细胞
吞噬灭活PAO1菌相对荧光强度定量图。两组比较,P < 0.001(n=3)。
*
图5 Pec1对MH⁃S细胞吞噬灭活铜绿假单胞菌PAO1的影响
Figure 5 Effect of the recombinant protein Pec1 on phagocytosis of heat⁃inactivated Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 by MH
⁃S cells
上述研究结果表明,巨噬细胞可通过促进或抑制自 [4] ZHU F,XIONG F,HE J,et al. Brd4 inhibition amelio⁃
噬,继而影响吞噬功能,最终影响胞内PA的清除。 rates pyocyanin ⁃ mediated macrophage dysfunction via
本研究初步观察到PA分泌的Pec1蛋白能够抑 transcriptional repression of reactive oxygen and nitrogen
free radical pathways[J]. Cell Death Dis,2020,11(6):
制MH⁃S巨噬细胞对灭活PA的吞噬,该分泌蛋白影
459
响吞噬的具体机制,是否对巨噬细胞自噬产生影响
[5] JAIN N,MOELLER J,VOGEL V. Mechanobiology of mac⁃
尚待进一步深入研究。 rophages:how physical factors coregulate macrophage
[参考文献] plasticity and phagocytosis[J]. Annu Rev Biomed Eng,
2019,2:267-297
[1] CURRAN C S,BOLIG T,TORABI ⁃ PARIZI P. Mecha⁃
[6] BARNES P J. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of asth⁃
nisms and targeted therapies for Pseudomonas aeruginosa
ma and COPD[J]. Clin Sci(Lond),2017,131(13):
lung infection[J]. Am J Respir Crit Care Med,2018,197
1541-1558
(6):708-727
[7] FELGNER S,PREUSSE M,BEUTLING U,et al. Host⁃in⁃
[2] 丁树红,金 菲,倪 芳,等. 下呼吸道感染患者支气管 duced spermidine production in motile Pseudomonas aeru⁃
肺泡灌洗液定量培养及临床分析[J]. 南京医科大学学 ginosa triggers phagocytic uptake[J]. Elife,2020,9:
报(自然科学版),2020,40(9):1354-1358 e55744
[3] HORCAJADA J P,MONTERO M,OLIVER A,et al. Epi⁃ [8] BIANCHI S M,PRINCE L R,MCPHILLIPS K,et al. Im⁃
demiology and treatment of multidrug⁃resistant and exten⁃ pairment of apoptotic cell engulfment by pyocyanin,a tox⁃
sively drug ⁃ resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections ic metabolite of Pseudomonas aeruginosa[J]. Am J
[J]. Clin Microbiol Rev,2019,32(4):e00019-e00031 Respir Crit Care Med,2008,177(1):35-43