Page 23 - 南京医科大学学报自然科学版
P. 23
第42卷第7期 祁颜艳,顾 愹,杨 涛. 负载HIP的耐受性树突状细胞对BDC2.5 T细胞的免疫调节作用[J].
2022年7月 南京医科大学学报(自然科学版),2022,42(7):913-920 ·919 ·
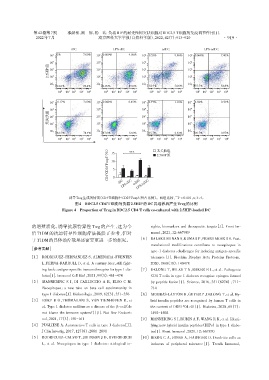
iDC LPS⁃iDC tolDC LPS⁃tolDC
10 5 0% 7.60% 10 5 0.009% 4.05% 10 5 0.55% 9.96% 10 5 0.068% 7.40%
10 4 10 4 10 4 10 4
2.5HIP组 10 3 2 10 3 2 10 3 2 10 3 2
10
10
10
10
101 101 101 101
14.0% 78.4% 6.96% 89.0% 54.9% 34.6% 37.7% 54.8%
1
1
1
1
10 0 10 10 2 10 3 10 4 10 0 10 10 2 10 3 10 4 10 0 10 10 2 10 3 10 4 10 0 10 10 2 10 3 10 4
10 5 4 0.17% 7.60% 10 5 4 0.022% 0.45% 10 5 4 0.77% 1.16% 10 5 4 4.82% 0.56%
10
10
10
无关肽组 10 3 2 10 3 2 10 3 2 10 3 2
10
10
10
10
10
101 101 101 101
82.5% 78.4% 87.6% 12.0% 95.7% 2.32% 96.7% 0.97%
1
1
1
1
10 0 10 10 2 10 3 10 4 10 0 10 10 2 10 3 10 4 10 0 10 10 2 10 3 10 4 10 0 10 10 2 10 3 10 4
( % ) 15 *** □ 无关肽组
■ 2.5HIP组
CD4 + CD25 + Foxp3 + 10 5
0
LPS⁃tolDC
iDC LPS⁃iDC tolDC
诱导Treg生成的情况(CD4 T细胞中CD25 Foxp3 所占比例)。两组比较, P < 0.001,n:3~4。
+
+
+
***
+
图4 BDC2.5 CD4 T细胞与负载2.5HIP的DC共培养后产生Treg的比例
Figure 4 Proportion of Treg in BDC2.5 CD4 T cells co⁃cultured with 2.5HIP⁃loaded DC
+
的增殖活化,诱导抗原特异性 Treg 的产生,这为今 sights,biomarkers and therapeutic targets[J]. Front Im⁃
后 T1DM 的抗原特异性细胞疗法提供了参考,但对 munol,2021,12:667989
于T1DM的具体治疗效果还需要更进一步的探究。 [6] BALAKRISHNAN S,KUMAR P,PRABHAKAR B S. Post⁃
translational modifications contribute to neoepitopes in
[参考文献]
type⁃1 diabetes:challenges for inducing antigen⁃specific
[1] RODRIGUEZ⁃FERNANDEZ S,ALMENARA⁃FUENTES tolerance[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta Proteins Proteom,
L,PERNA⁃BARRULL D,et al. A century later,still fight⁃ 2020,1868(10):140478
ing back:antigen⁃specific immunotherapies for type 1 dia⁃ [7] DELONG T,WILES T A,BAKER R L,et al. Pathogenic
betes[J]. Immunol Cell Biol,2021,99(5):461-474 CD4 T cells in type 1 diabetes recognize epitopes formed
[2] MANNERING S I,DI CARLUCCIO A R,ELSO C M. by peptide fusion[J]. Science,2016,351(6274):711-
Neoepitopes:a new take on beta cell autoimmunity in 714
type 1 diabetes[J]. Diabetologia,2019,62(3):351-356 [8] ARRIBAS⁃LAYTON D,GUYER P,DELONG T,et al. Hy⁃
[3] ROEP B O,THOMAIDOU S,VAN TIENHOVEN R,et brid insulin peptides are recognized by human T cells in
al. Type 1 diabetes mellitus as a disease of the β⁃cell(do the context of DRB1*04:01[J]. Diabetes,2020,69(7):
not blame the immune system?)[J]. Nat Rev Endocri⁃ 1492-1502
nol,2021,17(3):150-161 [9] MANNERING S I,RUBIN A F,WANG R K,et al. Identi⁃
[4] PUGLIESE A. Autoreactive T cells in type 1 diabetes[J]. fying new hybrid insulin peptides(HIPs)in type 1 diabe⁃
J Clin Investig,2017,127(8):2881-2891 tes[J]. Front Immunol,2021,12:667870
[5] RODRIGUEZ⁃CALVO T,JOHNSON J D,OVERBERGH [10] IBERG C A,JONES A,HAWIGER D. Dendritic cells as
L,et al. Neoepitopes in type 1 diabetes:etiological in⁃ inducers of peripheral tolerance[J]. Trends Immunol,