Page 76 - 南京医科大学学报自然科学版
P. 76
第43卷第6期
·818 · 南 京 医 科 大 学 学 报 2023年6月
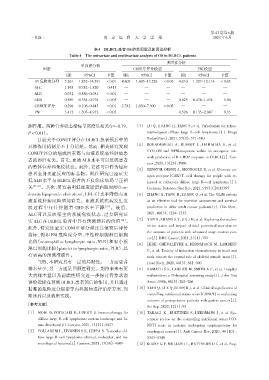
表4 DLBCL患者OS的单因素及多因素分析
Table 4 The univariate and multivariate analysis of OS in DLBCL patients
多因素分析
单因素分析
因素 CONUT评分模型 PNI模型
HR 95%CI P值 HR 95%CI P值 HR 95%CI P值
IPI危险度分型 5.261 1.852~14.591 <0.01 4.603 1.603~13.226 <0.01 4.010 1.327~12.114 <0.05
ALC 1.193 0.782~1.820 0.413 — — — — — —
ALB 0.932 0.886~0.981 <0.01 — — — — — —
CHO 0.589 0.354~0.978 <0.05 — — — 0.825 0.474~1.438 0.50
CONUT评分 0.298 0.106~0.843 <0.01 2.742 1.030~7.300 <0.05 — — —
PNI 3.412 1.303~8.932 <0.05 — — — 0.526 0.135~2.047 0.35
测作用。两种营养状态指标呈高度负相关(r=-0.79, [3] LU Q,HUANG H,TANG S,et al. Tafasitamab for refrac⁃
P<0.01)。 tory/relapsed diffuse large B⁃cell lymphoma[J]. Drugs
目前关于CONUT评分在DLBCL患者预后中的 Today(Barc),2021,57(9):571-580
具体作用机制并不十分清楚。然而,相关研究发现 [4] BOUROUMEAU A,BUSSOT L,HAMAIDIA S,et al.
CYCLON and NPM1cooperate within an oncogenic net⁃
CONUT 评分的组成因素都与血液系统恶性肿瘤患
work predictive of R⁃CHOP response in DLBCL[J]. Can⁃
者的预后有关。首先,血清ALB水平可以反映患者
cers,2021,13(23):5900
的整体营养和免疫状态。此外,它还可以作为癌症
[5] ERNST M,OESER A,BESIROGLU B,et al. Chimeric an⁃
患者全身炎症反应的标志物。既往研究已经证实
tigen receptor(CAR)T ⁃ cell therapy for people with re⁃
低 ALB 水平与 DLBCL 患者的不良临床结局呈正相
lapsed or refractory diffuse large B⁃cell lymphoma[J].
关 [25-26] 。其次,研究表明低密度脂蛋白胆固醇(low⁃ Cochrane Database Syst Rev,2021,9(9):CD013365
density lipoprotein cholesterol,LDL⁃C)水平降低与血 [6] ZHANG X,TANG M,ZHANG Q,et al. The GLIM criteria
液系统肿瘤风险增加有关。血液系统疾病发生发 as an effective tool for nutrition assessment and survival
展过程中往往伴随着 CHO 水平下降 [27] 。最后, prediction in older adult cancer patients[J]. Clin Nutr,
ALC 可以反映宿主的系统免疫状态,过去研究证 2021,40(3):1224-1232
实 ALC 在 DLBCL 患者中具有预测预后的价值 [28] 。 [7] YAN X,ZHANG S Y,JIA J M,et al. Exploring the malnu⁃
此外,研究还证实 CONUT 评分相比其他预后评价 trition status and impact of total parenteral nutrition on
the outcome of patients with advanced stage ovarian can⁃
指标,例如 PNI 危险度分型、中性粒细胞淋巴细胞
cer[J]. BMC Cancer,2021,21(1):799
比值(neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio,NLR)和血小板
[8] LERE⁃CHEVALEYRE A,BERNADACH M,LAMBERT
淋巴细胞比值(platelet to lymphocyte ratio,PLR),具
C,et al. Toxicity of induction chemotherapy in head and
有更高的预测准确性。 neck cancer:the central role of skeletal muscle mass[J].
当然,本研究具有一定的局限性。一方面患者 Head Neck,2021,44(3):681-690
样本量少,另一方面是回顾性研究。期待未来有更 [9] KAMATH S K,LAWLER M,SMITH A E,et al. Hospital
大的样本量以及前瞻性研究进一步探讨营养状态 malnutrition:a 33⁃hospital screening study[J]. J Am Diet
评价指标在预测DLBCL患者预后的作用,并且通过 Assoc,1986,86(2):203-206
精准的危险度分层指导内科医师选择治疗方案、判 [10] XIAO Q,LI X Q,DUAN B J,et al. Clinical significance of
断预后以及临床实践。 controlling nutritional status score(CONUT)in evaluating
outcome of postoperative patients with gastric cancer[J].
[参考文献]
Sci Rep,2022,12(1):93
[1] MODI D,POTUGARI B,UBERTI J. Immunotherapy for [11] TAKAGI K ,BUETTNER S,IJZERMANS J,et al. Sys⁃
diffuse large B⁃cell lymphoma:current landscape and fu⁃ tematic review on the controlling nutritional status(CO⁃
ture directions[J]. Cancers,2021,13(22):5827 NUT)score in patients undergoing esophagectomy for
[2] POLLARI M L,EIVONEN S K,LEPPA S. Testicular dif⁃ esophageal cancer[J]. Anti Cancer Res,2020,40(10):
fuse large B⁃cell lymphoma⁃clinical,molecular,and im⁃ 5343-5349
munological features[J]. Cancers,2021,13(16):4049 [12]BUZBY G P,MULLEN J L,MATTHEWS D C,et al. Prog⁃