Page 42 - 南京医科大学自然版
P. 42
第44卷第10期
·1358 · 南 京 医 科 大 学 学 报 2024年10月
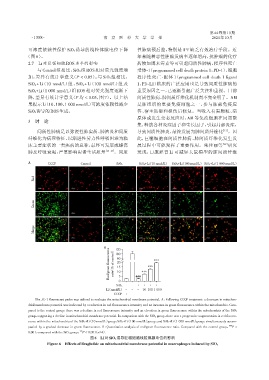
可浓度依赖性保护 SiO2诱导的线粒体膜电位下降 性肺病预后差,特别是 IPF 缺乏有效治疗手段。近
(图 6)。 年来随着恶性肿瘤发病率逐年增高,抗肿瘤的化疗
2.7 Li对巨噬细胞ROS水平的影响 药物如博来霉素等可引起间质性肺病,程序性死亡
与 Control 组相比,SiO2组 ROS 相对荧光强度增 受体⁃1(programmed cell death protein 1,PD⁃1)、细胞
加,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05);与 SiO2组相比, 程序性死亡⁃配体 1(programmed cell death 1 ligand
SiO2 +Li(10 nmol/L)组、SiO2 +Li(100 nmol/L)组及 1,PD⁃L1)临床的广泛应用也是导致间质性肺病的
SiO2+Li(1 000 nmol/L)组 ROS 相对荧光强度逐渐下 重要原因之一,已逐渐引起广泛关注和重视。目前
降,差异有统计学意义(P 均 < 0.05,图 7)。以上结 间质性肺病、肺间质纤维化机制尚不完全明了。AM
果提示Li(10、100、1 000 nmol/L)可浓度依赖性减少 是肺组织的重要免疫细胞之一,参与肺部免疫应
SiO2诱导的ROS生成。 答、宿主防御和损伤后修复。当吸入有害颗粒、病
原体或发生变态反应时,AM 等免疫细胞在局部聚
3 讨 论
集,释放各种炎症因子和生长因子,引起局部炎症,
间质性肺病是以弥漫性肺实质、肺泡炎和间质 导致间质性肺炎,最终发展为肺间质纤维化 [15] 。因
纤维化为病理特征,以渐进性劳力性呼吸困难为临 此,巨噬细胞在间质性肺病、肺间质纤维化发生发
床主要症状的一类疾病的总称,最终可发展成蜂窝 展过程中可能发挥了重要作用。朱佳丽等 [12] 研究
肺及呼吸衰竭,严重影响患者生活质量 [13-14] 。间质 发现,口服灌胃 Li 可减轻大鼠模型的肺间质纤维
A CCCP Control SiO2 SiO2+Li(10 nmol/L) SiO2+Li(100 nmol/L) SiO2+Li(1 000 nmol/L)
Red
Green
Merge
B 120
Red/green fluorescence (% of control) 80 *** *** ***
100
20
15
10
ratio
0 5 ###
SiO2 - - + + + +
Li(nmol/L) - - - 10 100 1 000
CCCP + - - - - -
The JC⁃1 fluorescent probe was utilized to evaluate the mitochondrial membrane potential. A:Following CCCP treatment,a decrease in mitochon⁃
drial membrane potential was indicated by a reduction in red fluorescence intensity and an increase in green fluorescence within the mitochondria. Com⁃
pared to the control group,there was a decline in red fluorescence intensity and an elevation in green fluorescence within the mitochondria of the SiO 2
group,suggesting a decline in mitochondrial membrane potential. In comparison with the SiO 2 group,there was a progressive augmentation in red fluores⁃
cence within the mitochondria of the SiO 2+Li(10 nmol/L)group,SiO2+Li(100 nmol/L)group,and SiO2+Li(1 000 nmol/L)group,simultaneously accom⁃
###
panied by a gradual decrease in green fluorescence. B:Quantitative analysis of red/green fluorescence ratio. Compared with the control group, P <
***
0.001;compared with the SiO 2 group, P < 0.001(n=4).
图6 Li对SiO2诱导巨噬细胞线粒体膜电位的影响
Figure 6 Effects of liraglutide on mitochondrial membrane potential in macrophages induced by SiO 2