Page 87 - 南京医科大学自然版
P. 87
第44卷第11期 谷志远,蔡 赟,陈欢欢,等. SurePath沉降式液基细胞采集技术应用于甲状腺细针穿刺细胞学诊断的
2024年11月 准确性评价[J]. 南京医科大学学报(自然科学版),2024,44(11):1550-1557,1580 ·1553 ·
表1 SurePath⁃LBC病理诊断为SM、M与组织病理对比分析
Table 1 Comparison analysis between SurePath⁃LBC pathological diagonsis of SM and M cases and histopathologially con⁃
firmed M cases
Cytology Number Histology Number Consistency rate(%) Total consistency rate(%)
SM Suspicious PTC 110 PTC 106 96.4 97.3
FTC 001
WT⁃UMP 002
Atypical adenoma 001
Suspicious MTC 002 MTC 002 100
M PTC 210 PTC 209 99.5 99.5
Atypical hyperplasia 001
MTC 001 MTC 001 100
SM:suspicious for malignancy. M:malignant. PTC:papillary thyroid carcinoma. MTC:medullary thyroid carcinoma. FTC:follicular thyroid carcino⁃
ma. WT⁃UMP:well differentiated tumors of uncertain malignant potential.
A B C D
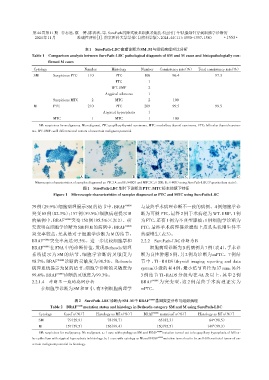
Microscopic characteristics of samples diagnosed as PTC(A and B,×400)and MTC(C,× 200;D,× 400)using SurePath⁃LBC(Papanicolaou stain).
图1 SurePath⁃LBC制片下诊断为PTC、MTC标本的镜下特征
Figure 1 Microscopic characteristics of samples diagnosed as PTC and MTC using SurePath⁃LBC
V600E 与最终手术病理诊断不一致的病例。4例细胞学诊
79例(29.9%)细胞病理提示SM的结节中,BRAF
突变 65 例(82.3%);157 例(59.5%)细胞病理提示 M 断为可疑 PTC,最终 2 例手术病理为 WT⁃UMP,1 例
的病例中,BRAF V600E 突变 150 例(95.5%)(表 2)。研 为 FTC,还有 1 例为不典型腺瘤;1 例细胞学诊断为
究表明在细胞学诊断为SM和M的病例中,BRAF V600E PTC,最终手术病理提示滤泡上皮乳头状增生伴不
突变率较高,尤其是对于细胞学诊断为 M 的结节, 典型增生(表3)。
BRAF V600E 突变率高达95.5%。进一步比较细胞学和 2.2.2 SurePath⁃LBC诊断为B
BRAF V600E 在 FNA 中的诊断价值,发现 Bethesda 病理 细胞病理诊断为B的病例共7例(表4),手术诊
系统提示为 SM 的结节,细胞学诊断的灵敏度为 断为良性肿瘤 5 例,另 2 例均诊断为 mPTC。7 例结
V600E
98.7%,BRAF 诊断的灵敏度为 98.5%。Bethesda 节 中 ,TI ⁃ RADS(thyroid imaging reporting and data
病理系统提示为M的结节,细胞学诊断的灵敏度为 system)3 级的有 4 例,最小结节直径为 37 mm;另外
99.4%,BRAF V600E 诊断的灵敏度为99.3%。 3 例结节 TI⁃RADS 分级均在 4A 及以上,其中 2 例
2.2.1.4 诊断不一致的病例分析 BRAF V600E 为突变型,这 2 例最终手术病理证实为
在细胞学诊断为SM和M中,有5例细胞病理学 mPTC。
表2 SurePath⁃LBC诊断为SM、M中BRAF V600E 基因突变分布与组织病理
Table 2 BRAF V600E mutation status and histology in Bethesda category SM and M using SurePath⁃LBC
Cytology Case[n(%)] Histology as M[n(%)] BRAF V600E mutation[n(%)] Histology as M[n(%)]
a
SM 079(29.9) 078(98.7) 065(82.3) 064(98.5)
b
M 157(59.5) 156(99.4) 150(95.5) 149(99.3)
SM:suspicious for malignancy. M:malignant. a:1 case with cytology as SM and BRAF V600E mutation turned out to be papillary hyperplasia of follicu⁃
lar epithelium with atypical hyperplasia in histology. b:1 case with cytology as M and BRAF V600E mutation turned out to be well differentiated tumor of un⁃
certain malignant potential in histology.