Page 115 - 南京医科大学学报自然科学版
P. 115
第44卷第3期 孙 芃,高俊英. 脑膜免疫在中枢神经系统疾病中的研究进展[J].
2024年3月 南京医科大学学报(自然科学版),2024,44(3):398-409 ·405 ·
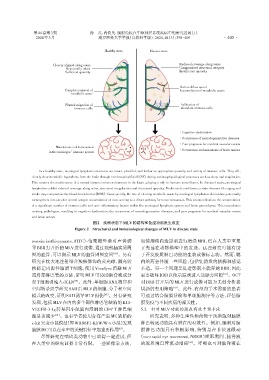
Healthy state Disease state
Reduced coverage along veins
Closely aligned along veins
Compromised structural integrity
Structurally intact
Insufficient quantity
Sufficient quantity
Reduced flow speed
Complete removal of Accumulation of metabolic waste
metabolic waste
Normal migration of Infiltration of
immune cells abundant immune cells
·Cognitive dysfunction
·Occurrence of neurodegenerative diseases
·Poor prognosis for cerebral vascular events
Maintenance of homeostasis
·Occurrence and metastasis of brain tumors
in the meninges’immune system
In a healthy state,meningeal lymphatic structures are intact,plentiful,and harbor an appropriate quantity and variety of immune cells. They effi⁃
ciently clear metabolic byproducts from the brain through cerebrospinal fluid(CSF)during various physiological processes such as sleep and respiration.
This ensures the maintenance of a normal immune microenvironment in the brain,playing a role in immune surveillance. In diseased states,meningeal
lymphatics exhibit reduced coverage along veins,structural irregularities and decreased quantity. Under such conditions,certain diseases like aging and
stroke may compromise the blood⁃brain barrier(BBB). Consequently,the rate of clearing metabolic waste by meningeal lymphatics diminishes,potentially
turning them into sites for central antigen accumulation or even serving as a direct pathway for tumor metastasis. This situation leads to the accumulation
of a significant number of immune cells and anti⁃inflammatory factors within the meningeal lymphatic system and brain parenchyma. This exacerbates
existing pathologies,resulting in cognitive dysfunction,the occurrence of neurodegenerative diseases,and poor prognosis for cerebral vascular events
and brain tumors.
图2 疾病状态下MLV的结构和免疫功能发生改变
Figure 2 Struchural and immunological changes of MLV in disease state
rescein isothiocyanate,FITC)⁃葡聚糖外渗对声音诱 如使用鞘内造影剂进行增强 MRI,已在人类中重复
导BBB打开后的MLV进行成像,通过观察脑实质周 了先前在动物模型中的发现。这些研究可能有助
围的血管,可以揭示MLV的血管周围空间 [62] 。另有 于开发胶质淋巴功能的生物成像标志物。然而,鞘
研究在枕大池注射结合羧酸修饰的荧光球,激光转 内给药会伴随一些风险,包括钆诱发的脑病和感觉
换标记内源性脑膜 T 细胞,使用 Visudyne 消融 MLV 不适。另一个问题是钆造影剂不能穿越 BBB,因此
或鼻部淋巴管的方法,证明MLV可协助脑脊液成分 需要破坏BBB以使示踪剂进入动脉旁间隙 [61] 。OCT
如T细胞引流入dCLN 。此外,单细胞RNA测序和 对 BBB 打开后的 MLV 进行成像可能为无创分析提
[18]
空间转录组学研究SAH后MLV的细胞、分子和空间 供新的有用策略 [62] 。此外,有颅内手术需要的患者
模式的改变,证明SAH诱导MLV损伤 [63] 。另有研究 可通过结合脑膜活检和单细胞测序等方法,评估脑
发现,包括MLV在内的多个部位淋巴管缺陷的K14⁃ 膜免疫与不同疾病的相关性。
VEGFR⁃3⁃Ig 转基因小鼠脑内浸润的 CD4 T 淋巴细 5.2 针对MLV功能的潜在有效干预手段
+
胞显著减少 [64] 。也有学者使用存在严重MC缺陷的 研究表明,多种生理性和药物干预措施对脑膜
c⁃kit突变小鼠模型(即WBB6F1⁃KitW/W⁃v小鼠)发现 淋巴转运功能具有潜在的有效性。例如,睡眠对脑
脑膜MC可以在卒中的关键特征中起重要作用 。 膜淋巴功能具有积极影响,特别是在非快速眼动
[65]
尽管研究在啮齿类动物中已取得一定进展,但 (non⁃rapid eye movement,NREM)睡眠期间,脑脊液
在人类中的研究证据非常有限。一些影像学方法, 的胶质淋巴管流动增强 [66] 。呼吸也可对脑脊液在