Page 53 - 南京医科大学自然版
P. 53
第44卷第7期 徐 杰,王 喆,张忠满,等. 细菌性肝脓肿合并糖尿病患者出现脓毒性休克的危险因素分析[J].
2024年7月 南京医科大学学报(自然科学版),2024,44(7):934-940 ·937 ·
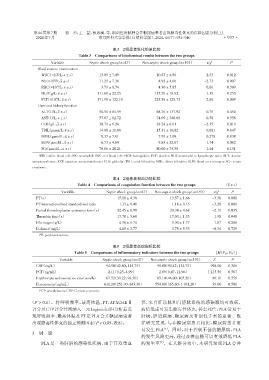
表3 2组患者生化结果比较
Table 3 Comparisons of biochemical results between the two groups
Variable Septic shock group(n=47) Non⁃septic shock group(n=193) t/χ 2 P
Blood routine examination
WBC(×10 /L,x ± s) 13.09 ± 7.490 10.83 ± 4.860 -2.53 0.012
9
NE(×10 /L,x ± s) 11.29 ± 7.380 8.92 ± 4.66 -2.73 0.007
9
RBC(×10 /L,x ± s) 3.73 ± 0.74 4.30 ± 5.85 -0.66 0.509
12
HGB(g/L,x ± s) 111.60 ± 22.250 115.29 ± 18.920 -1.15 0.250
PLT(×10 /L,x ± s) 171.95 ± 122.18 225.38 ± 125.73 -2.66 0.009
9
Liver and kidney function
ALT(U/L,x ± s) 58.51 ± 61.59 068.76 ± 137.92 -0.75 0.450
AST(U/L,x ± s) 57.67 ± 82.72 074.09 ± 346.68 -0.58 0.558
GLB(g/L,x ± s) 30.79 ± 6.260 28.24 ± 6.610 -2.35 0.019
TBIL(μmol/L,x ± s) 14.08 ± 10.08 15.31 ± 10.82 -0.681 0.847
DBIL(μmol/L,x ± s) 8.37 ± 7.01 7.99 ± 7.08 -0.278 0.838
BUN(μmol/L,x ± s) 6.73 ± 4.69 09.85 ± 22.67 -1.74 0.082
SCr(μmol/L,x ± s) 70.66 ± 28.21 80.60 ± 75.58 -1.44 0.151
WBC:white blood cell;NE:neutrophil;RBC:red blood cell;HGB:hemoglobin;PLT:platelet;NLR:neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio;ALT:alanine
aminotransferase;AST:aspartate aminotransferase;GLB:globulin;TBIL:total bilirubin;DBIL:direct bilirubin;BUN:blood urea nitrogen;SCr:serum
creatinine.
表4 2组患者凝血功能比较
Table 4 Comparisons of coagulation function between the two groups (x ± s)
Variable Septic shock group(n=47) Non⁃septic shock group(n=193) t/χ 2 P
PT(s) 15.10 ± 4.38 13.57 ± 1.66 -3.38 0.001
PT internationalized standardized ratio 01.33 ± 0.48 01.18 ± 0.15 -3.28 0.001
Partial thromboplastin activation time(s) 32.45 ± 8.99 30.34 ± 4.68 -2.11 0.035
Thrombin time(s) 17.70 ± 3.68 17.00 ± 1.35 -1.98 0.048
Fibrinogen(g/L) 04.98 ± 1.74 05.30 ± 1.77 1.07 0.286
D⁃dimer(mg/L) 04.15 ± 3.77 03.75 ± 5.33 -0.34 0.729
PT:prothrombin time.
表5 2组患者炎症指标比较
Table 5 Comparisons of inflammatory indicators between the two groups [M(P25,P75)]
Variable Septic shock group(n=47) Non⁃septic shock group(n=193) Z P
CRP(mg/L) 94.50(42.80,115.75) 98.00(50.42,134.75)0 998.00 0.386
PCT(ng/mL) 2.11(0.25,4.99)00 2.09(0.47,12.96)0 0 1 215.50 0.567
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate(mm/h) 67.52(30.22,98.30)0 85.10(46.00,105.20)0 89.10 0.556
Ferroprotein(ng/mL) 611.20(251.90,843.30) 554.00(365.60,1 101.20) 39.00 0.501
PCT:procalcitonin;CRP:C⁃reactive protein.
(P > 0.1)。将呼吸频率、最高体温、PT、APACHEⅡ 供,来自肝动脉和门静脉系统的感染源均可致病,
评分及CTP评分共同纳入二元Logistic回归分析后发 病情危重可发生脓毒性休克,甚至死亡,PLA常见于
现呼吸频率、最高体温及PT是PLA合并糖尿病患者 肝病、胆道疾病、糖尿病及有创性手术的患者。既
出现脓毒性休克的独立预测因素(P < 0.05,表8)。 往研究发现,与非糖尿病患者相比,糖尿病患者更
[6]
易发生 PLA 。同时,对于控制不佳的糖尿病,PLA
3 讨 论
的发生风险更高,通过改善血糖可以有效降低 PLA
[7]
PLA 是一类肝脏的感染性疾病,由于其双重血 的发生率 。在人群分布中,本研究发现 PLA 合并