Page 29 - 南京医科大学自然版
P. 29
第44卷第8期 罗 浙,练雷栋,胡珂琦,等. CPO⁃PCL微粒在缺氧条件下对脂肪间充质干细胞体外增殖及成骨
2024年8月 分化作用的影响[J]. 南京医科大学学报(自然科学版),2024,44(8):1051-1061 ·1057 ·
A
CPO⁃PCL
Control 0.10% 0.25% 0.50% 1.00%
Hypoxia and
Hypoxia and osteogenic normal culture
Osteogenic differentiation culture 5 4 *** *** *** 1.5
differentiation culture
RUNX2 Relative fluorescence 0 intensity of RUNX2 3 2 1 Relative fluorescence intensity of RUNX2 1.0
0.5
Normal culture Control 0.10% 0.25% 0.50% 1.00% 0 Control 0.10% 0.25% 0.50% 1.00%
CPO⁃PCL CPO⁃PCL
B
CPO⁃PCL
Control 0.10% 0.25% 0.50% 1.00%
Hypoxia and osteogenic normal culture
Hypoxia and
differentiation culture
Osteogenic differentiation culture 15 *** *** 8 6 *** ***
10
Osteocalcin Relative fluorescence intensity of Osteocalcin 5 *** Relative fluorescence intensity of Oosteocalcin 4 2 *** ***
Normal culture 0 Control 0.10% 0.25% 0.50% 1.00% 0 Control 0.10% 0.25% 0.50% 1.00%
C CPO⁃PCL CPO⁃PCL CPO⁃PCL
Control 0.10% 0.25% 0.50% 1.00%
Hypoxia and osteogenic normal culture
Hypoxia and
Osteogenic differentiation culture 30 *** 25 ***
differentiation culture
20
Osteopontin Relative fluorescence intensity of Osteopontin 10 * *** *** Relative fluorescence intensity of Osteopontin 15 5 * *** ***
20
10
Normal culture 0 Control 0.10% 0.25% 0.50% 1.00% 0 Control 0.10% 0.25% 0.50% 1.00%
CPO⁃PCL
CPO⁃PCL
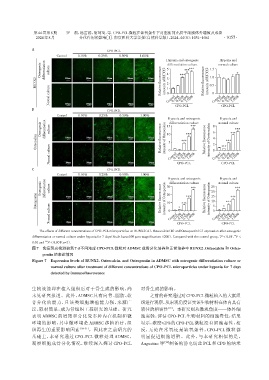
The effects of different concentrations of CPO⁃PCL microparticles on RUNX2(A),Osteocalcin(B)and Osteopontin(C)expression after osteogenic
*
**
differentiation or normal culture under hypoxia for 7 days(Scale bars=100 μm;magnification:×200). Compared with the control group,P < 0.05,P <
0.01 and *** P < 0.001(n=3).
图7 免疫荧光检测缺氧7 d不同浓度CPO⁃PCL微粒对ADMSC成骨分化培养和正常培养中RUNX2、Osteocalcin 和 Osteo⁃
pontin的表达情况
Figure 7 Expression levels of RUNX2,Osteocalcin,and Osteopontin in ADMSC with osteogenic differentiation culture or
normal culture after treatment of different concentrations of CPO⁃PCL microparticles under hypoxia for 7 days
detected by immunofluorescence
生物效能即在植入组织后对于骨生成的影响,尚 对骨生成的影响。
未见研究报道。此外,ADMSC 具有向骨、脂肪、软 之前的研究通过对CPO⁃PCL微粒植入的大鼠组
骨分化的能力,且该类细胞增殖能力强、来源广 织进行观察,从宏观角度证实该生物材料在体内具有
泛、取材简单,成为骨组织工程研究的基础。研究 较佳的相容性 。本研究则从微观角度——体外细
[19]
表明 ADMSC 的增殖和分化受多种内在机制和微 胞实验,评估 CPO⁃PCL 生物材料的细胞毒性,结果
环境的影响,其中微环境是 ADMSC 移植治疗、组 显示,浓度≤1%的CPO⁃PCL微粒没有细胞毒性,相
织再生的重要影响因素 [20-21] 。因此在之前研究的 反,无论在常氧还是缺氧条件,CPO⁃PCL 微粒都
基础上,本研究通过 CPO⁃PCL 微粒处理 ADMSC, 明显促进细胞增殖。此外,与本研究相似的是,
观察细胞成骨分化情况,继续深入探讨 CPO⁃PCL Augustine 等 [22] 制备的静电纺丝 PCL 和 CPO 的纳米