Page 31 - 南京医科大学自然版
P. 31
第44卷第8期 罗 浙,练雷栋,胡珂琦,等. CPO⁃PCL微粒在缺氧条件下对脂肪间充质干细胞体外增殖及成骨
2024年8月 分化作用的影响[J]. 南京医科大学学报(自然科学版),2024,44(8):1051-1061 ·1059 ·
A
CPO⁃PCL
Control 0.10% 0.25% 0.50% 1.00%
Hypoxia and osteogenic Hypoxia and normal
Osteogenic differentiation culture 15 *** 10 8 ***
differentiation culture
culture
RUNX2 Relative fluorescence intensity of RUNX2 10 5 * ** *** Relative fluorescence intensity of RUNX2 6 4 2 ** ***
Normal culture 0 Control 0.10% 0.25% 0.50% 1.00% 0 Control 0.10% 0.25% 0.50% 1.00%
CPO⁃PCL CPO⁃PCL
B CPO⁃PCL
Control 0.10% 0.25% 0.50% 1.00%
Hypoxia and osteogenic Hypoxia and normal
Osteogenic differentiation culture 8 6 *** 8 6 *** ***
culture
differentiation culture
Osteocalcin Relative fluorescence intensity of Osteocalcin 4 2 *** Relative fluorescence intensity of Osteocalcin 4 2 ** ***
Normal culture 0 Control 0.10% 0.25% 0.50% 1.00% 0 Control 0.10% 0.25% 0.50% 1.00%
C CPO⁃PCL CPO⁃PCL CPO⁃PCL
Control 0.10% 0.25% 0.50% 1.00%
Hypoxia and osteogenic Hypoxia and normal
Osteogenic differentiation culture 15 *** 15 ***
culture
differentiation culture
Osteopontin Relative fluorescence intensity of Osteopontin 10 5 *** ** *** Relative fluorescence intensity of Osteopontin 10 5 ** *** ***
Normal culture 0 Control 0.10% 0.25% 0.50% 1.00% 0 Control 0.10% 0.25% 0.50% 1.00%
CPO⁃PCL CPO⁃PCL
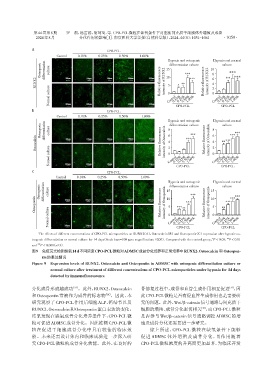
The effects of different concentrations of CPO⁃PCL microparticles on RUNX2(A),Osteocalcin(B)and Osteopontin(C)expression after hypoxic os⁃
*
**
teogenic differentiation or normal culture for 14 days(Scale bars=100 μm;magnification:×200). Compared with the control group,P < 0.05,P < 0.01
and *** P < 0.001(n=3).
图9 免疫荧光检测缺氧14 d不同浓度CPO⁃PCL微粒对ADMSC成骨分化培养和正常培养中RUNX2、Osteocalcin 和 Osteopon⁃
tin的表达情况
Figure 9 Expression levels of RUNX2,Osteocalcin and Osteopontin in ADMSC with osteogenic differentiation culture or
normal culture after treatment of different concentrations of CPO⁃PCL microparticles under hypoxia for 14 days
detected by immunofluorescence
[23]
分化成骨形成越成功 [27] 。此外,RUNX2、Osteocalcin 骨修复过程中,成骨和血管生成作用相互促进 ,因
和Osteopontin 常被作为成骨的标志物 [28] 。因此,本 此CPO⁃PCL微粒是否有促血管生成作用也是需要研
研究观察了CPO⁃PCL 作用后细胞ALP、钙结节以及 究的问题。此外,Wnt/β⁃catenin信号通路与间充质干
RUNX2、Osteocalcin和Osteopontin蛋白表达的变化, 细胞的增殖、成骨分化密切相关 ,而CPO⁃PCL微粒
[29]
结果发现在缺氧成骨分化培养条件下,CPO⁃PCL 微 是否参与 Wnt/β⁃catenin 信号通路调控 ADMSC 的增
粒可促进ADMSC成骨分化。因此推测CPO⁃PCL微 殖及成骨分化还需要进一步研究。
粒在促进干细胞成骨分化中具有较佳的临床效 综上所述,CPO⁃PCL 微粒在缺氧条件下能够
能。未来还需设计体内和临床试验进一步深入研 促进 ADMSC 体外增殖及成骨分化,且作用随着
究CPO⁃PCL微粒的成骨分化效能。此外,在良好的 CPO⁃PCL微粒浓度的升高而更加显著,为临床开发