Page 13 - 南京医科大学自然版
P. 13
第44卷第11期 何晓鑫,高俊英,郭吉超,等. Bmi⁃1基因杂合子缺失对小鼠脑老化的影响[J].
2024年11月 南京医科大学学报(自然科学版),2024,44(11):1473-1482 ·1479 ·
A B C D
NeuN PCNA DCX Caspase⁃3
WT
Bmi⁃1 +/-
E 30 000 * WT +/- F 1 200 WT +/- G (%) 6 5 WT +/-
Positive cells in DG 20 000 Positive cells in SGZ 800 * * Apoptosis cells in DG 4 3 2
25 000
Bmi⁃1
Bmi⁃1
Bmi⁃1
1 000
15 000
600
10 000
400
5 000
0 200 0 1 0
NeuN
PCNA DCX Caspase⁃3
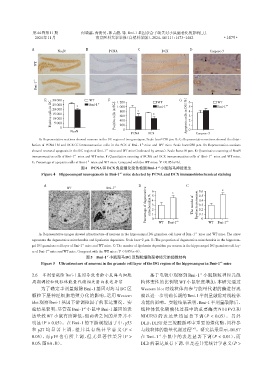
A:Representative sections showed neurons in the DG region of two genotypes. Scale bars=150 μm. B,C:Representative sections showed the distri⁃
+/⁃
bution of PCNA(B)and DCX(C)immunoreactive cells in the SGZ of Bmi⁃ 1 mice and WT mice. Scale bars=250 μm. D:Representative sections
+/-
showed neuronal apoptosis in the DG region of Bmi⁃1 mice and WT mice(indicated by arrows). Scale bars=10 μm. E:Quantitative counting of NeuN
immunoreactive cells of Bmi⁃1 +/- mice and WT mice. F:Quantitative counting of PCNA and DCX immunoreactive cells of Bmi⁃1 +/- mice and WT mice.
*
+/-
G:Percentage of apoptotic cells of Bmi⁃1 mice and WT mice. Compared with the WT mice,P < 0.05(n=6).
+/-
图4 PCNA和DCX免疫组化染色检测Bmi⁃1 小鼠海马神经发生
Figure 4 Hippocampal neurogenesis in Bmi⁃1 mice detected by PCNA and DCX immunohistochemical staining
+/-
A B C
Percentage of degenerative 1 mitochondria 4 3 2 0 The numbe of lipofuscin perneuron 0.4 0
WT Bmi⁃1 +/- 6 5 % * 0.6 *
0.5
0.3
0.2
0.1
+/-
+/-
WT
Bmi⁃1
Bmi⁃1
WT
A:Representative images showed ultrastructure of neurons in the hippocampal DG granulosa cell layer of Bmi⁃1 +/- mice and WT mice. The arrow
represents the degenerative mitochondria and lipofuscin deposition. Scale bars=2 μm. B:The proportion of degenerative mitochondria in the hippocam⁃
+/-
pal DG granulosa cell layer of Bmi⁃1 mice and WT mice. C:The number of lipofuscin deposition per neuron in the hippocampal DG granulosa cell lay⁃
+/-
*
er of Bmi⁃1 mice and WT mice. Compared with the WT mice,P < 0.05(n=6).
+/-
图5 Bmi⁃1 小鼠海马DG区颗粒细胞层神经元的超微结构
Figure 5 Ultrastructure of neurons in the granule cell layer of the DG region of the hippocampus in Bmi⁃1 mice
+/-
+/-
2.6 半剂量敲除Bmi⁃1基因导致老龄小鼠海马细胞 基于电镜中观察到 Bmi⁃1 小鼠颗粒神经元线
周期调控和线粒体能量代谢相关蛋白表达异常 粒体变性的比例较 WT 小鼠轻度增加,本研究通过
为了确定半剂量敲除 Bmi⁃1 基因对海马 DG 区 Western blot 对线粒体内参与能量代谢的酶进行观
颗粒下层神经细胞增殖分化的影响,运用 Western 察以进一步明确长期的Bmi⁃1半剂量敲除对线粒体
blot 观察 Bmi⁃1 基因下游调控因子的表达情况。实 功能的影响。实验结果表明,Bmi⁃1半剂量敲除后,
验结果表明,尽管在Bmi⁃1 小鼠中Bmi⁃1基因的表 线粒体氧化磷酸化过程中的重要酶类 NDUFV2 和
+/-
达量较 WT 小鼠有所降低,但两者之间的差异并不 NDUFS3 的表达量均显著下调(P < 0.05)。另外
明显(P > 0.05)。在 Bmi⁃1 的下游调控因子中,p53 DLD、DLST 是三羧酸循环中重要的催化酶,同样参
和 p27 均 显 著 上 调 ,差 异 具 有 统 计 学 意 义(P < 与线粒体的能量代谢过程 [16] 。研究结果显示,DLST
+/-
0.05),而 p19 也有所上调,但无显著性差异(P > 在 Bmi⁃1 小鼠中的表达显著下调(P < 0.01),而
0.05,图6A、B)。 DLD 的表达虽有下调,但是差异无统计学意义(P >