Page 37 - 南京医科大学学报自然科学版
P. 37
第44卷第2期 石诺林,倪中亚,袁富文. 基于网络药理学及实验研究探讨臭椿皮散治疗结直肠癌的潜在机制[J].
2024年2月 南京医科大学学报(自然科学版),2024,44(2):170-177,184 ·175 ·
表1 臭椿皮散抗结直肠癌核心靶点的拓扑参数 渐降低,呈现出剂量依赖性(图8)。
Table 1 Topological parameters of CCPS anti⁃CRC core
targets 3 讨 论
Target Degree Betweenness Closeness
结直肠癌患者临床上主要表现为便秘、腹胀、
MAPK1 10 4.459 627 329 0.727 272 727
腹痛、腹泻,严重者出现血便、呕吐,若肿瘤转移至
MAPK14 11 12.159 834 370 0.761 904 762
其他器官还可能出现其他疾病,严重影响患者生存
AKT1 10 8.366 873 706 0.727 272 727
MYC 11 7.423 809 524 0.761 904 762 质量和生存时间。中医药在结直肠癌诊断治疗过
HIF1A 11 12.406 211 180 0.761 904 762 程中的优势和特色明显,具有丰富的临床经验。臭
CDKN1A 9 8.127 536 232 0.695 652 174
椿皮散作为临床上治疗结直肠癌的经典中医方剂,
FOS 10 5.492 960 663 0.727 272 727
对其药理机制的研究显得尤为迫切。
IP53 10 12.704 968 940 0.727 272 727
ESP1 11 11.606 211 180 0.761 904 762 本文基于网络药理学方法,共筛选出 117 种潜
RB1 6 2.400 000 000 0.592 592 593 在药物成分和787个共同作用蛋白靶点。在臭椿皮
EGFR 7 1.266 666 667 0.615 384 615
散治疗结直肠癌的核心基因靶点筛选发现,基因关
STAT1 7 3.465 631 470 0.640 000 000
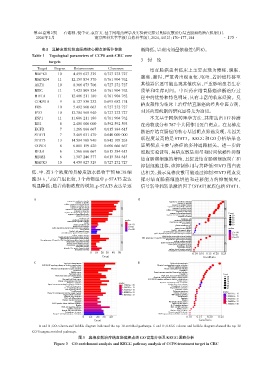
联程度最高的是 STAT3。KEGG 和 GO 分析结果也
STAT3 13 14.504 968 940 0.842 105 263
证明靶点主要与癌症的多种通路相关。进一步的
CCND1 8 6.081 159 420 0.666 666 667
RELA 6 1.566 666 667 0.615 384 615 细胞实验证明,臭椿皮散呈剂量和时间依赖性抑制
MDM2 6 1.507 246 377 0.615 384 615
结直肠癌细胞的增殖,且促进结直肠癌细胞凋亡和
MAPK3 10 4.459 627 329 0.727 272 727
抑制细胞迁移,该抑制作用与其降低STAT3蛋白表
低、中、高 3 个浓度的臭椿皮散水提物干预 MC38 细 达相关,提示臭椿皮散可能通过抑制STAT3靶点发
胞 24 h,与空白组比较,3 个药物组中 p⁃STAT3 表达 挥对结直肠癌细胞增殖和迁移能力的抑制效应。
明显降低;随着药物浓度的增加,p⁃STAT3表达量逐 信号转导和转录激活因子(STAT)家族包括STAT1、
A B
response to xenobiotic stimulus response to xenobiotic stimulus
response to peptide
response to peptide
cellular response to chemical stress response to oxidative stress
response to oxidative stress response to extracellular stimulus
response to nutrient leveis response to nutrient leveis
response to extracellular stimulus BP cellular response to chemical stress BP
response to metal ion
response to metal ion
response to reactive oxygen species response to lipopolysaccharide Count
response to lipopolysaccharide response to reactive oxygen species
response to ketone response to ketone 10
membrane raft 20
membrane raft
membrane microdomain qvalue membrane microdomain 30
transcription regulator complex transcription regulator complex
caveola 40
vesicl lumem
plasma membrane raft 5.0e-07 plasma membrane raft 50
protein kinase complex CC 1.0-08 caveola CC
cyclin⁃dependent protein kinase holoenzyme complex protein kinase complex qvalue
vesicl lumem 1.5e-08
ficolin⁃1⁃rich granule lumen
ficolin⁃1⁃rich granule lumen serine/threonine protein kinase complex
serine/threonine protein kinase complex cyclin⁃dependent protein kinase holoenzyme complex 1.5e-08
nuclear receptor activity 1.0-08
ligand⁃activated transcription factor activity DNA⁃binding transcription factor binding 5.0e-07
DNA⁃binding transcription factor binding RNA polymerase Ⅱ⁃specific DNA⁃binding transcription factor binding
Rna polymerase Ⅱ⁃specific DNA⁃binding transcription factor binding ubiquitin⁃like protein ligase binding
transcription coregulator binding NF nuclear receptor activity
nuclear steroid receptor activity ligand⁃activated transcription factor activity NF
transcription coactivator binding transcription coregulator binding
antioxidant activity phosphatase binding
antioxidant activity
ubiquitin⁃like protein ligase binding nuclear steroid receptor activity
phosphatase binding
transcription coactivator binding
0 10 20 30 40 50
0.05 0.10 0.15 0.20 0.25
Count GeneRatio
C Lipid and atherosclerosis D Lipid and atherosclerosis
AGE⁃RAGE signaling pathway in diabetic complications Chemical carcinogenesis⁃receptor activation
Prostate cancer PI3K⁃Akt signaling pathway
Chemical carcinogenesis⁃receptor activation Human cytomegalovirus infection
Hepatitis B Hepatitis B
Bladder cancer Kaposi sarcoma⁃associated herpesvirus infection
Pancreatic cancer Hepatitis C Count
Fluid shear stress and atherosclerosis Fluid shear stress and atherosclerosis
Hepatitis C Chemical carcinogenesis⁃reactive oxygen species 20
Non⁃small cell lung cancer AGE⁃RAGE signaling pathway in diabetic complications 25
Human cytomegalovirus infection Prostate cancer 30
Endocrine resistance qvalue Human T⁃cell leukmia virus 1 infection
Kaposi sarcoma⁃associated herpesvirus infection 1.738661e-30 Epstein⁃Barr virus infection 35
Small cell lung cancer Proteoglycans in cancer 40
IL⁃17 signaling pathway 1.966283e-15 Hepatocellular carcinoma 45
TNF signaling pathway 3.932566e-15 Pancreatic cancer
Toxoplasmosis Endocrine resistance qvalue
Chemical carcinogenesis⁃reactive oxygen species 5.898849e-15 Cellular senescence 7.865132e-15
Hepatocellular carcinoma 7.865132e-15 TNF signaling pathway
Platinum drug resistance Toxoplasmosis 5.898849e-15
Th17 cell differentiation Apoptosis 3.932566e-15
Choronic myeloid leukemia Measies
Apoptosis Non⁃small cell lung cancer 1.966283e-15
EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance Small cell lung cancer 1.738661e-30
Measles IL⁃17 signaling pathway
PI3K⁃Akt signaling pathway Th17 cell differentiation
Cellular senescence Bladder cancer
Epstein⁃Barr virus infection Platinum drug resistance
Proteoglycans in cancer Choronic myeloid leukemia
Human T⁃cell leukemia virus 1 infection EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance
0 10 20 30 40 0.10 0.15 0.20 0.25
Count GeneRatio
A and B:GO column and bubble diagram indicated the top 10 enriched pathways. C and D:KEGG column and bubble diagram showed the top 30
CCPS targets enriched pathways.
图3 臭椿皮散治疗结直肠癌靶点的GO富集分析及KEGG通路分析
Figure 3 GO enrichment analysis and KEGG pathway analysis of CCPS treatment target in CRC