Page 23 - 南京医科大学自然版
P. 23
第44卷第6期 张赟豪,韩博昂,王 瑜,等. SENP1在SPOP去SUMO化修饰中的作用研究[J].
2024年6月 南京医科大学学报(自然科学版),2024,44(6):753-761 ·759 ·
A Flag⁃Spop Flag⁃Spop⁃K95R Flag⁃Spop⁃K110R Flag⁃Spop⁃K95/110R
WT
Senp1 -/-
B Cytoplasm C Cytoplasm
* 10 Nuclear 10 10 Nuclear
10 * * ***
* *** *** *** ***
PLA signals per cell 5 PLA signals per cell 5 PLA signals per cell 5 PLA signals per cell 5 ***
0 0 0 0
Flag⁃Spop Flag⁃Spop⁃K95R Flag⁃Spop⁃K110R Flag⁃Spop⁃K95/110R Flag⁃Spop Flag⁃Spop⁃K95R Flag⁃Spop⁃K110R Flag⁃Spop⁃K95/110R Flag⁃Spop Flag⁃Spop⁃K95R Flag⁃Spop⁃K110R Flag⁃Spop⁃K95/110R Flag⁃Spop Flag⁃Spop⁃K95R Flag⁃Spop⁃K110R Flag⁃Spop⁃K95/110R
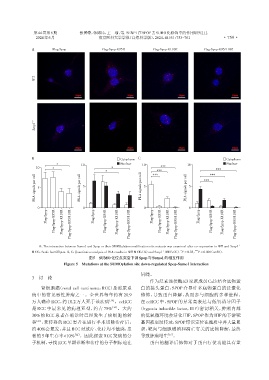
A:The interaction between Sumo1 and Spop or their SUMOylation modification site mutants was examined after co⁃expression in WT and Senp1 -/-
-/-
***
*
MEFs. Scale bar=20 μm. B,C:Quantitative analysis of PLA results in WT MEFs(B)and Senp1 MEFs(C). P < 0.05, P < 0.001(n=50).
图5 SUMO化位点突变下调Spop与Sumo1的相互作用
Figure 5 Mutations at the SUMOylation site down⁃regulated Spop⁃Sumo1 interaction
眉睫。
3 讨 论
作为泛素连接酶 E3 家族成员 Cul3 结合底物蛋
肾细胞癌(renal cell carcinoma,RCC)是泌尿系 白的接头蛋白,SPOP 介导许多底物蛋白的泛素化
统中的常见恶性肿瘤之一。全世界每年约有 20.9 修饰,导致蛋白降解,从而参与细胞的多种进程。
万人确诊 RCC,约 10.2 万人死于该疾病 [19] 。ccRCC 在 ccRCC 中,SPOP 的异常高表达与低氧诱导因子
是 RCC 中最常见的病理亚型,约占 75% [20] 。大约 (hypoxia inducible factor,HIF)密切相关,肿瘤内部
30%的 RCC 患者在确诊时已经发生了癌细胞的转 的低氧微环境会活化HIF,SPOP作为HIF的下游靶
移 [21] ,未转移的 RCC 患者在进行手术切除治疗后, 基因被启动转录,SPOP错误定位在胞质中并大量累
约40%会复发,并且RCC对放疗、化疗均不敏感,患 积,靶向与细胞增殖和凋亡有关的底物降解,最终
[15]
者的 5 年生存率<10% [22] 。因此探索 RCC 发病的分 导致肿瘤增生 。
子机制,寻找RCC早期诊断和治疗的分子靶标迫在 蛋白的翻译后修饰对于蛋白行使功能具有重