Page 61 - 南京医科大学学报自然科学版
P. 61
第43卷第11期 卢 英,雍景超,吴志奇. 甲胎蛋白阴性肝细胞癌患者的预后分析[J].
2023年11月 南京医科大学学报(自然科学版),2023,43(11):1527-1534 ·1533 ·
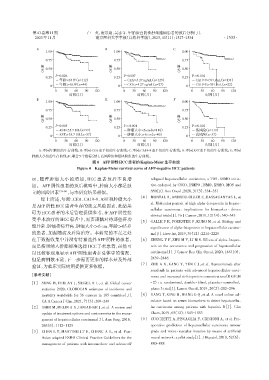
A B C
1.00 1.00 1.00
0.75 0.75 0.75
OS率 0.50 OS率 0.50 OS率 0.50
P=0.026 P=0.007 P<0.001
0.25 0.25 0.25
年龄≤65岁(n=112) CEA≤4.27 ng/mL(n=129) CA19⁃9≤39 U/mL(n=134)
年龄>65岁(n=44) CEA>4.27 ng/mL(n=27) CA19⁃9>39 U/mL(n=22)
0 0 0
0 30 60 90 120 0 30 60 90 120 0 30 60 90 120
时间(月) 时间(月) 时间(月)
D E F
1.00 1.00 1.00
0.75 0.75 0.75
OS率 0.50 OS率 0.50 OS率 0.50
P=0.005 P<0.001 P<0.001
0.25 0.25 0.25
AST≤35.7 U/L(n=99) 肿瘤大小≤6 cm(n=116) 低风险(n=119)
AST>35.7 U/L(n=57) 肿瘤大小>6 cm(n=40) 高风险(n=37)
0 0 0
0 30 60 90 120 0 30 60 90 120 0 30 60 90 120
时间(月) 时间(月) 时间(月)
A:不同年龄组的生存曲线;B:不同 CEA水平组的生存曲线;C:不同 CA19⁃9水平组的生存曲线;D:不同AST水平组的生存曲线;E:不同
肿瘤大小组的生存曲线;F:联合5个指标分组,高风险组和低风险组的生存曲线。
图4 AFP阴性HCC患者的Kaplan⁃Meier生存曲线
Figure 4 Kaplan⁃Meier survival curve of AFP⁃negative HCC patients
示,随着肿瘤大小的增加,HCC 患者预后不良增 relapsed hepatocellular carcinoma:a TOS ⁃ ESMO initia⁃
加。 AFP阴性患者的预后模型中,肿瘤大小都是独 tive endorsed by CSCO,ISMPO,JSMO,KSMO,MOS and
立的风险因素 [33-34] ,与本研究结果相似。 SSO[J]. Ann Oncol,2020,31(3):334-351
综上所述,年龄、CEA、CA19⁃9、AST和肿瘤大小 [4] MONTAL R,ANDREU⁃OLLER C,BASSAGANYAS L,et
al. Molecular portrait of high alpha⁃fetoprotein in hepato⁃
是AFP阴性HCC患者生存的独立风险因素,此结果
cellular carcinoma:implications for biomarker ⁃ driven
可为HCC患者的术后管理提供参考,在AFP阴性接
clinical trials[J]. Br J Cancer,2019,121(4):340-343
受手术治疗的HCC患者中,需要谨慎对待那些肝功
[5] GALLE P R,FOERSTER F,KUDO M,et al. Biology and
能异常、肿瘤指标升高、肿瘤大小>6 cm、年龄>65岁 significance of alpha⁃fetoprotein in hepatocellular carcino⁃
的患者,加强随访及后续治疗。本研究的不足之处 ma[J]. Liver Int,2019,39(12):2214-2229
在于数据收集中并没有特意选择AFP阴性的患者, [6] ZHENG Y F,ZHU M Y,LI M S. Effects of alpha⁃fetopro⁃
而是按照纳入排除标准选择HCC手术患者,虽然可 tein on the occurrence and progression of hepatocellular
以比较客观地显示AFP阴性患者在总体中的情况, carcinoma[J]. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol,2020,146(10):
但是病例数不足,下一步需要更多的样本量及外部 2439-2446
验证,为临床实际应用提供更多依据。 [7] ZHU A X,KANG Y,YEN C J,et al. Ramucirumab after
sorafenib in patients with advanced hepatocellular carci⁃
[参考文献]
noma and increased α⁃fetoprotein concentrations(REACH
[1] SUNG H,FERLAY J,SIEGEL R L,et al. Global cancer ⁃ 2):a randomised,double ⁃ blind,placebo ⁃ controlled,
statistics 2020:GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and phase 3 trial[J]. Lancet Oncol,2019,20(2):282-296
mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. [8] YANG T,XING H,WANG G Q,et al. A novel online cal⁃
CA A Cancer J Clin,2021,71(3):209-249 culator based on serum biomarkers to detect hepatocellu⁃
[2] DHIR M,MELIN A A,DOUAIHER J,et al. A review and lar carcinoma among patients with hepatitis B[J]. Clin
update of treatment options and controversies in the mana⁃ Chem,2019,65(12):1543-1553
gement of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Ann Surg,2016, [9] CUCCHETTI A,PISCAGLIA F,GRIGIONI A,et al. Pre⁃
263(6):1112-1125 operative prediction of hepatocellular carcinoma tumour
[3] CHEN L T,MARTINELLT E,CHENG A L,et al. Pan ⁃ grade and micro⁃vascular invasion by means of artificial
Asian adapted ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for the neural network:a pilot study[J]. J Hepatol,2010,52(6):
management of patients with intermediate and advanced/ 880-888