Page 13 - 南京医科大学学报自然科学版
P. 13
第44卷第1期 肖心儒,范 亮,施宇佳,等. A2M在慢性阻塞性肺疾病中的表达及其与免疫细胞浸润的
2024年1月 相关性[J]. 南京医科大学学报(自然科学版),2024,44(01):001-011,059 · 7 ·
A
100
B cells naive
B cells memory
Plasma cells
T cells CD8
80 T cells CD4 naive
T cells CD4 memory resting
( % ) 60 T cells CD4 memory activated
T cells follicular helper
T cells regulatory(Tregs)
Relative percent 40 NK cells resting
T cells gamma delta
NK cells activated
Monocytes
Macrophages M0
Macrophages M1
Macrophages M2
Dendritic cells resting
Dendritic cells activated
20 Mast cells resting
Mast cells activated
Eosinophils
Neutrophils
0
Control COPD
B C
Control COPD
* ** ** *
0.3
Fraction 0.2 Correlation
0.1 A2M * ** * 0.4
0.2
0.0
-0.2
0
B cells naive B cells memory Plasma cells T cells CD8 T cells CD4 memory resting T cells CD4 naive T cells CD4 memory activated T cells follicular helper ( Tregs) T cells regulatory T cells gamma delta NK cells resting NK cells activated Monocytes Macrophages M0 Macrophages M1 Macrophages M2 Dendritic cells resting Dendritic cells activated Mast cells resting Mast cells activated Eosinophils Neutrophils B cells memory B cells naive Dendritic cells a
T cells CD4 memory activated
T cells follicular helper
T cells CD4 memory resting
T cells regulatory
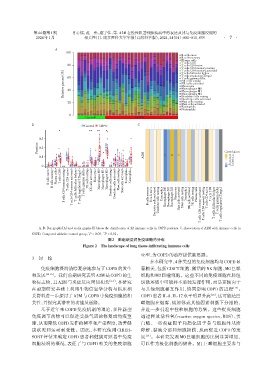
A,B:Bar graphs(A)and violin graphs(B)show the distribution of 22 immune cells in COPD patients. C:Association of A2M with immune cells in
COPD. Compared with the control group,P < 0.05,P < 0.01。
**
*
图2 肺组织浸润免疫细胞的分布
Figure 2 The landscape of lung tissue⁃infiltrating immune cells
亚型,为COPD的治疗提供新思路。
3 讨 论
在本研究中,4种类型的免疫细胞均与COPD显
免疫细胞浸润错综复杂地参与了COPD的发生 著相关,包括 CD8 T 细胞、激活的 NK 细胞、M0 巨噬
+
和发展 [14-16] 。我们前期研究表明A2M是COPD的生 细胞和M2巨噬细胞。这些不同的免疫细胞在肺组
物标志物,且A2M与炎症反应密切相关 [8-9] ,本研究 织微环境中可能并不单独发挥作用,而是更倾向于
在前期研究基础上利用生物信息学分析与临床相 与其他细胞相互作用,协同影响 COPD 的进程 [17] 。
关资料进一步探讨了A2M与COPD中免疫细胞的相 COPD患者IL⁃8、IL⁃17水平明显升高 [18] ,这可能是巨
关性,并探究其潜在的功能及通路。 噬细胞在烟雾、病原体或其他因素刺激下分泌的,
基于近年来 COPD 免疫机制的理论,多种新型 并进一步引起中性粒细胞的募集。这些促炎细胞
免疫调节药物可以促进受损气道的修复或免疫重 通过释放活性氧(reactive oxygen species,ROS)、蛋
建,从而降低COPD发作的频率和严重程度,改善健 白酶、一些炎症因子和趋化因子参与细胞外基质
康状况和运动耐受性。因此,本研究使用 CIBER⁃ 降解、黏液分泌和细胞损伤,从而促进 COPD 的发
SORT 评估来确定 COPD 患者和健康对照者中免疫 展 [19] 。本研究发现 M0 巨噬细胞的比例显著增加,
细胞浸润的概况,表征了与 COPD 相关的免疫细胞 可以作为极化刺激的储备。M1 巨噬细胞主要参与