Page 70 - 南京医科大学自然版
P. 70
第44卷第4期
·508 · 南 京 医 科 大 学 学 报 2024年4月
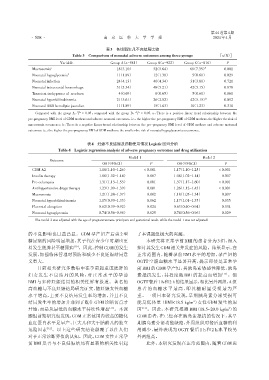
表3 各组新生儿不良结局比较
Table 3 Comparison of neonatal adverse outcomes among three groups [n(%)]
Variable Group A(n=581) Group B(n=922) Group C(n=816) P
Macrosomia a 18(3.10) 52(5.64) 60(7.35) # 0.001
Neonatal hypoglycemia b 11(1.89) 12(1.30) 05(0.61) 0.029
Neonatal infection 24(4.13) 40(4.34) 31(3.80) 0.721
Neonatal intracranial hemorrhage 31(5.34) 48(5.21) 42(5.15) 0.878
Transient tachypnoea of newborn 04(0.69) 06(0.65) 05(0.61) 0.861
Neonatal hyperbilirubinemia 21(3.61) 26(2.82) 42(5.15) △ 0.092
Neonatal ABO hemolytic jaundice 11(1.89) 15(1.63) 10(1.23) 0.310
#
△
Compared with the group A,P < 0.05;compared with the group B, P < 0.05. a:There is a positive linear trend relationship between the
pre⁃pregnancy BMI level of GDM mothers and adverse neonatal outcomes,i.e.,the higher the pre⁃pregnancy BMI of GDM mothers,the higher the risk of
macrosomia occurrence. b:There is a negative linear trend relationship between the pre⁃pregnancy BMI level of GDM mothers and adverse maternal
outcomes,i.e.,the higher the pre⁃pregnancy BMI of GDM mothers,the smaller the risk of neonatal hypoglycaemia occurrence.
表4 妊娠不良结局及药物使用情况Logistic回归分析
Table 4 Logistic regression analysis of adverse pregnancy outcomes and drug utilization
Model 1 Model 2
Outcome
OR(95%CI) P OR(95%CI) P
GDM A2 1.18(1.10-1.26) < 0.001 1.17(1.10-1.25) < 0.001
Insulin therapy 1.08(1.02-1.14) 0.007 1.08(1.02-1.14) 0.007
Pre⁃eclampsia 1.31(1.13-1.53) 0.001 1.37(1.17-1.60) < 0.001
Antihypertensive drugs therapy 1.23(1.09-1.39) 0.001 1.26(1.12-1.43) < 0.001
Macrosomia 1.21(1.08-1.37) 0.002 1.18(1.05-1.34) 0.007
Neonatal hyperbilirubinemia 1.15(0.99-1.33) 0.062 1.17(1.01-1.35) 0.035
Placental abruption 0.62(0.39-0.92) 0.024 0.63(0.40-0.94) 0.034
Neonatal hypoglycemia 0.74(0.56-0.96) 0.025 0.74(0.56-0.96) 0.029
The model 2 was adjusted with the age of pregnant women,primipara and gestational week,while the model 1 was not adjusted.
的不良影响也日益凸显。GDM 孕产妇产后患 2 型 了本课题组极大的兴趣。
糖尿病的风险明显增加,其子代在青少年时期也更 本研究将正常孕前 BMI 的患者分为 3 组,深入
易发生肥胖甚至糖尿病 [10] 。因此,控制GDM的发生 探讨其发生GDM相关并发症的风险。结果显示,在
发展,加强临床管理对预防和减少不良妊娠结局意 正常范围内,随着孕前 BMI 水平的增加,孕产妇的
义重大。 OGTT 空腹血糖水平显著升高,提示即使是正常孕
目前相关研究多数集中在孕前超重或肥胖的 前 BMI 的 GDM 孕产妇,其胰岛素敏感性降低,胰岛
妇女发生不良结局的风险,对正常水平的孕前 素抵抗发生,其程度随 BMI 的提高而增加 [13] 。但
BMI 与多种妊娠结局的相关性鲜有报道。著名的 OGTT餐后1 h和2 h的结果显示,相比另外两组,A组
高血糖与不良妊娠结局研究证实,随妊娠女性血糖 患者的血糖水平最高,即其糖耐量受损最为严
水平增高,主要不良结局发生率均增加,并且不良 重。一项日本研究发现,早期胰岛素分泌受损可
结局发生率的增加并非到了既往 GDM 诊断切点才 能是低体重(BMI<18.5 kg/m )女性 GDM 发生的原
2
开始,而是从最低的血糖水平持续性增加 [11] 。本课 因 [14] 。因此,本研究推测 BMI(18.5~20.0 kg/m )的
2
题组前期研究也发现,GDM正常范围内较高的糖化 GDM 患者,在已经存在胰岛素抵抗的情况下,其早
血红蛋白水平是早产、巨大儿和大于胎龄儿的独立 期胰岛素分泌功能缺陷,外周组织对餐后血糖的利
危险因素 [12] 。以上这些研究结论颠覆了以往人们 用减少,最终表现为 OGTT 餐后 1 h 和 2 h 水平较另
对于正常诊断界值的认知。因此,GDM女性正常孕 外两组高。
前 BMI 是否与不良妊娠结局有显著的相关性引起 此外,本研究发现在正常范围内,随着 GDM 患