Page 15 - 南京医科大学自然版
P. 15
第44卷第5期 曾 强,张在奎,孙乃双,等. TBK1对NLRC4炎症小体的作用及其机制研究[J].
2024年5月 南京医科大学学报(自然科学版),2024,44(5):595-603,614 ·603 ·
A B C D E
500 *** 400 *** 60 *** 60 ** (CFU/mL) 150 000 *
(pg/mL) 400 (pg/mL) 300 (pg/mL) 40 (pg/mL) 40 100 000
300
Serum IL⁃β 200 PCF IL⁃1β 200 Serum TNF⁃α 20 PCF TNF⁃α 20 Bacterial load in PCF 50 000
100
100
0 0 0 0 0
S.T S.T+AML S.T S.T+AML S.T S.T+AML S.T S.T+AML S.T S.T+AML
F G H
100 000 *** (%) 40 **
Bacterial load in lung (CFU/mL) tissues 60 000 CD11b 20.0 CD11b 6.79 cells CD11b + /Ly6G + 30
80 000
20
40 000
10
20 000
0 0
S.T S.T+AML Ly6G Ly6G S.T S.T+AML
S.T S.T+AML
I *
(%) 100 S.T
S.T+AML
Survival rate 50
0
0 50 100 150 200
Time(h)
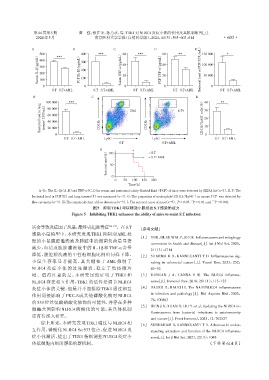
A-D:The IL⁃1β(A,B)and TNF⁃α(C,D)in serum and peritoneal cavity⁃flushed fluid(PCF)of mice were detected by ELISA kit(n=3). E,F:The
+
+
bacterial load in PCF(E)and lung tissues(F)was measured(n=3). G:The proportion of neutrophils(CD11b /Ly6G )in mouse PCF was detected by
* ** ***
flow cytometry(n=3). H:The statistical chart of flow detection(n=3). I:The survival curve of mice(n=5). P < 0.05,P < 0.01,and P < 0.001.
图5 抑制TBK1可以增强小鼠抵抗S.T感染的能力
Figure 5 Inhibiting TBK1 enhances the ability of mice to resist S.T infection
活会导致炎症因子风暴,最终引起脓毒症 [16-17] 。在S.T [参考文献]
感染小鼠模型中,本研究发现 TBK1 抑制剂 AML 处
[1] YUK J M,SILWAL P,JO E K. Inflammasome and mitophagy
理的小鼠腹腔灌洗液及肺脏中的细菌负荷量显著
connection in health and disease[J]. Int J Mol Sci,2020,
减少,血清及腹腔灌洗液中的 IL⁃1β和 TNF⁃α含量
21(13):4714
降低,腹腔灌洗液的中性粒细胞比例也同样下降,
[2] SHARMA B R,KANNEGANTI T D. Inflammasome sig⁃
小鼠生存率显著提高,其关键在于 AML 抑制了 naling in colorectal cancer[J]. Transl Res,2023,252:
NLRC4 炎症小体的过度激活,稳定了免疫微环 45-52
境。值得注意的是,本研究虽然证明了 TBK1 和 [3] DUNCAN J A ,CANNA S W. The NLRC4 inflamma⁃
NLRC4 存在相互作用,TBK1 的活性是调节 NLRC4 some[J]. Immunol Rev,2018,281(1):115-123
炎症小体的关键,但是并不能排除 TBK1 通过相互 [4] BAUER R,RAUCH I. The NAIP/NLRC4 inflammasome
in infection and pathology[J]. Mol Aspects Med,2020,
作用间接影响了 PKC⁃δ或其他磷酸化酶对 NLRC4
76:100863
的 533 位丝氨酸磷酸化修饰的可能性,并存在多种
[5] WEN J X,XUAN B,LIU Y,et al. Updating the NLRC4 in⁃
激酶共同影响 NLRC4 磷酸化的可能,其具体机制
flammasome:from bacterial infections to autoimmunity
还有待深入研究。
and cancer[J]. Front Immunol,2021,12:702527
综上所述,本研究发现 TBK1 通过与 NLRC4 相
[6] SUNDARAM B,KANNEGANTI T D. Advances in under⁃
互作用,磷酸化 NLRC4 Ser533 位点,促进 NLRC4 炎
standing activation and function of the NLRC4 inflamma⁃
症小体激活,提出了 TBK1 精细调控 NLRC4 炎症小 some[J]. Int J Mol Sci,2021,22(3):1048
体抵御胞内细菌感染的新机制。 (下转第614页)