Page 104 - 南京医科大学自然版
P. 104
第44卷第11期
·1570 · 南 京 医 科 大 学 学 报 2024年11月
A B Subgroup Tislelizumab+CT CT OS HR(95%Cl)
All Patients NR 19.3 0.4(0.2-0.7)
Sex
Male NR 19.0 0.4(0.2-0.8)
Female NR 20.1 0.2(0.0-2.0)
Age
< 65 years NR 19.3 0.3(0.1-0.7)
≥65 years NR 19.0 0.5(0.2-1.2)
Smoking status
Current/former NR 17.5 0.3(0.1-0.6)
100 Never NR 21.5 0.4(0.1-1.2)
(%) 75 ECOG status NR 19.0 0.3(0.2-0.6)
PS 0-1
Overall survival 50 TNM stage 24.7 18.5 0.2(0.1-0.6)
0.8(0.1-6.0)
23.2
NR
PS 2
NR
Ⅲ
0.9(0.3-2.3)
21.5
Ⅳ
25
CT
PC
Tislelizumab+CT Chemotherapy regimes NR 25.1 0.7(0.2-1.9)
0 nab⁃PC NR 19.0 0.2(0.1-0.4)
0 6 12 18 24 30 36 Distantmetastaticorgan
Time(months) Brain 24.7 24.2 1.0(0.1-9.4)
Bone 18.8 21.5 1.1(0.2-6.8)
Lung 24.7 21.3 0.9(0.1-6.1)
Number of metastatic site
1-3 NR 19.8 0.3(0.1-0.9)
4-7 18.8 25.4 1.3(0.1-12.8)
0.1 1.0 10.0
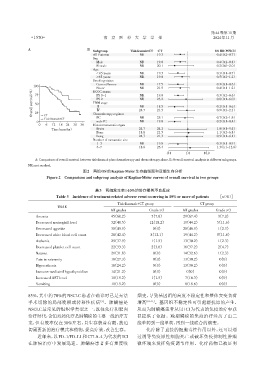
A:Comparison of overall survival between tislelizumab plus chemotherapy and chemotherapy alone. B:Overall survival analysis in different subgroups.
NR:not reached.
图2 两组OS的Kaplan⁃Meier生存曲线图和亚组生存分析
Figure 2 Comparison and subgroup analysis of Kaplan⁃Meier curves of overall survival in two groups
表3 两组发生率≥10%的治疗相关不良反应
Table 3 Incidence of treatment⁃related adverse event occurring in 10% or more of patients [n(%)]
Tislelizumab+CT group CT group
TRAE
All grades Grade ≥3 All grades Grade ≥3
Anemia 45(68.2) 5(7.6) 29(67.4) 3(7.0)
Decreased neutrophil level 32(48.5) 12(18.2) 19(44.2) 5(11.6)
Decreased appetite 30(45.5) 0(0) 20(46.5) 1(2.3)
Decreased white blood cell count 28(42.4) 8(12.1) 19(44.2) 5(11.6)
Asthenia 25(37.9) 1(1.5) 13(30.2) 1(2.3)
Decreased platelet cell count 22(33.3) 2(3.0) 16(37.2) 2(4.7)
Nausea 21(31.8) 0(0) 14(32.6) 1(2.3)
Pain in extremity 18(27.3) 0(0) 13(30.2) 0(0)
Hypoesthesia 16(24.2) 0(0) 13(30.2) 0(0)
Immune⁃mediated hypothyroidism 14(21.2) 0(0) 0(0) 0(0)
Increased AST level 10(15.2) 1(1.5) 07(16.3) 0(0)
Vomiting 10(15.2) 0(0) 08(18.6) 0(0)
85%,其中约 70%的 NSCLC 患者在确诊时已是无法 烟史,导致基因组的高度不稳定性和整体突变负荷
手术切除的局部晚期或转移性疾病 。肺鳞癌是 增高 [10-11] 。基因组不稳定性可引起新抗原的产生,
[9]
NSCLC最常见的组织学类型之一,既往化疗和靶向 从而为肺鳞癌患者从以ICI为代表的免疫治疗中获
治疗时代,含铂双药化疗是肺鳞癌的主要一线治疗方 益提供了依据。晚期鳞癌的免疫治疗经历了由二
案,但有效率仅在30%左右,且生存获益有限,故迫 线单药到一线单药,再到一线联合的演变。
切需要新的治疗模式和药物,提高疗效,改善生存。 化疗除了直接的细胞毒性作用以外,还可以通
近年来,以PD⁃1/PD⁃L1和CTLA⁃4为代表的ICI 过诱导免疫原性细胞死亡或破坏免疫抑制性肿瘤
在肺癌治疗中发展迅速。肺鳞癌患者多有重度吸 微环境来发挥免疫调节作用。化疗药物已被证明